データセンター、商業・産業用途の蓄電池 2026-2036年:市場、予測、プレーヤー、技術Battery Storage for Data Centers, Commercial & Industrial Applications 2026-2036: Market, Forecasts, Players, Technology データセンターおよびC&Iアプリケーション用BESSの10年詳細予測。プレーヤー、主要プロジェクト、アプリケーション、蓄電池技術動向、ベンチマーク、LFPリチウムイオンコスト、製造に関する分析。数十件... もっと見る

サマリー
データセンターおよびC&Iアプリケーション用BESSの10年詳細予測。プレーヤー、主要プロジェクト、アプリケーション、蓄電池技術動向、ベンチマーク、LFPリチウムイオンコスト、製造に関する分析。数十件の一次インタビューから得られた知見
データセンター、通信基地局(5G、6G)、電気自動車(EV)充電、建設、農業、鉱業、その他工場、病院、地域社会、災害救援などの重要なアプリケーションなど、幅広い産業で定置型商業・産業用(C&I)バッテリー蓄電システム(BESS)のバッテリー需要が伸びています。これらの市場において、C&I BESSは、無停電電源装置(UPS)、ピークカット、マイクログリッド、使用時間の裁定、グリッドの柔軟性、データセンターにおける揮発性の人工知能(AI)計算負荷の管理など、様々なアプリケーションで使用されている。IDTechExは、これらの産業全体で、2036年までに世界のC&I BESS市場は210億米ドルに達すると予測している。
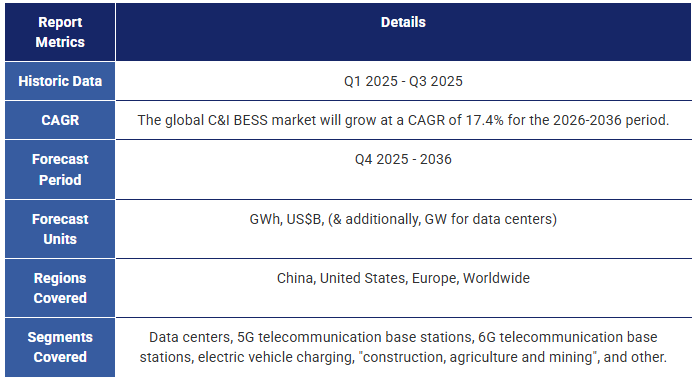
商業用および産業用蓄電池アプリケーションの概要。出典:IDTechEx:IDTechEx.
C&I BESSアプリケーションと市場概要
商業・産業用(C&I)バッテリーストレージ市場は、特に、より確立されたグリッドスケールや家庭用バッテリーストレージ市場と比較して、伝統的にニッチセグメントとみなされてきた。しかし、この状況は今後10年間で変化し、2026年から2036年の間にC&I BESS需要は約5倍の成長が見込まれる。C&I BESSプレーヤーは、CATL、BYD、テスラといった既存のリチウムイオンBESS大手から市場シェアを奪うためには、それに応じて適応しなければならない。本レポートは、C&I BESSプレーヤーへの数十回に及ぶ一次インタビューから得られた知見を提供し、プロジェクト、ターゲットとするアプリケーション、バッテリー技術に関する独自の洞察を提供する。
短期的には、データセンター向けBESSは、特に米国とヨーロッパで急速に成長するアプリケーションになる。時間の経過とともに、世界的な需要は6Gの展開をサポートする中国にシフトするだろう。5G(サブ6GHz)タワーと6Gタワーには、大規模なマクロタワーが配備される(だろう)。これらはネットワーク・バックボーンの重要なノードと考えられ、鉛蓄電池であれリチウムイオン電池であれ、あるいは長時間の停電をカバーするためのディーゼル発電機であれ、ほとんど常にUPS/バックアップ電源用のバッテリーを備えている。次の10年の終わりには、欧米以外の農業や建設業でEVの普及が進むため、EV充電をサポートするC&I BESSがこれらの現場に配備されることになる。
データセンター用
蓄電池 サーバー、ストレージ、ネットワーク機器などの重要な負荷を少なくともカバーするため、蓄電池需要はデータセンターの電力需要に密接に追随するだろう。ハイパースケールの人工知能(AI)データセンターの規模が拡大するにつれて、無停電電源装置(UPS)用のバッテリーの電力要件と容量も増加する。これにより、データセンターはサービスレベル契約に従ってオンライン状態を維持し、データ損失を防ぐことができます。そうでなければ、多額の金銭的損失、セキュリティ問題、主要サービスの中断を引き起こす可能性があります。
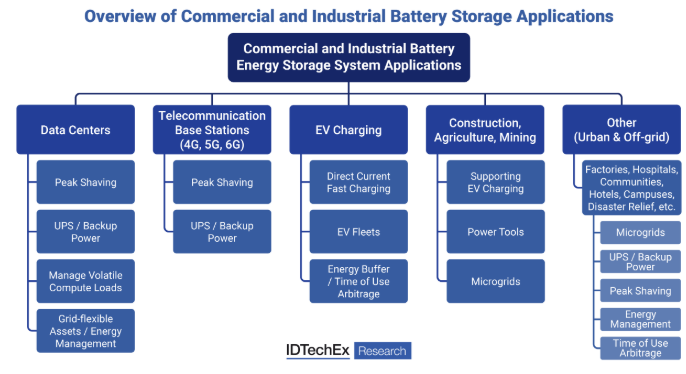
データセンターにおけるバッテリー・ストレージの他の重要な用途のひとつは、揮発性のAIコンピュート負荷を管理することである。このようなMW規模の電力需要の変動に対抗するために、データセンターのオペレータは、電力網から安定した電力を供給できるように、余分なオペレーションを実行することで、より高い連続電力でデータセンターを稼働させることができる。しかし、これは電力の無駄遣いであり、運用コストを増加させる。その代わりに、電力コストを削減するために、電力供給が過剰なときに充電し、電力需要が増加したときにデータセンターに放電することで、この変動を平滑化するために蓄電池を使用することができる。
データセンターからの電力需要の変動。出典:IDTechEx:IDTechEx.
データセンターでは従来、UPS用にバルブ制御鉛蓄電池(VRLA)が使用されてきたが、リチウムイオンのサイクル寿命の長さとコストの低下により、これらの技術は着実にVRLAバッテリーを駆逐している。しかし、リチウムイオンバッテリーの主な欠点には、劣化や可燃性電解液による安全性のリスクがあります。1日に何度も繰り返し使用されるため、データセンターからの引退が早まる可能性がある。レドックス・フロー・バッテリー(RFB)のような他のバッテリー・ストレージ技術は、長時間のサイクルでも劣化が少ないため、揮発性のAIコンピューティング負荷の管理に適しているかもしれない。また、RFBは不燃性の電解液を使用しており、データセンターでリチウムイオン電池の火災が発生していることを考えると、これは重要な利点である。実際、データセンターの規模が拡大するにつれて、データセンター施設の広範なエネルギー管理戦略の一環として、RFBのような長時間のバッテリー貯蔵技術が必要になる可能性があります。本レポートでは、費用対効果分析、利用戦略、今後のバッテリー技術採用など、データセンターにおけるバッテリーストレージの主な動向について詳述する。
商業用・産業用蓄電池技術
リチウムイオン技術のコストは低下し続けており、欧米ではデータセンター用BESSの需要が急増していることから、中国への依存度を下げるために国内のリチウムイオン供給チェーンの構築が重要となっている。米国における45倍の製造業生産税額控除やOBBBA(One Big Beautiful Bill Act)を通じて、米国におけるLFPリチウムイオン電池の生産は、商業用や産業用を含む米国内のすべてのリチウムイオンBESS市場に供給するための鍵となる。IDTechExの本レポートは、米国におけるLFP製造能力の動向と、2026年以降、関税のかかる中国製LFPセルの輸入と比較した、税額控除の影響による米国製LFPセルのコストに関する定量的コスト分析を提供している。
IDTechExは、リチウムイオン電池以外に、C&I用途に開発されているNaイオン電池、VRLA電池、セカンドライフEV電池、レドックスフロー電池を観察してきた。すべての技術には、コスト、エネルギー密度、サイクル寿命、安全性、応答時間に関する長所と短所がある。本レポートでは、これらのBESS技術をベンチマークし、C&I電池エネルギー貯蔵アプリケーションへの適合性について論じる。主要メーカーのリチウムイオンC&I BESS技術をベンチマークし、C&IリチウムイオンBESSのコストを構成要素別に提供する。
予測
本レポートは、2025年から2036年までの世界の商業用および産業用BESS市場の10年間の市場予測を、用途別、地域別にGWh需要および市場価値(US$B)ごとに詳細に記載している。地域別アプリケーション別GWh予測も掲載。データセンターにおけるGW別BESSの予測を地域別に提供。
企業プロファイル
このIDTechExレポートには、C&I BESS企業、主要リチウムイオンBESS企業、代替電池貯蔵技術(レドックスフロー電池、Naイオン、セカンドライフEV、VRLA、亜鉛ベース電池など)を開発する企業を含む30以上の企業プロファイルが含まれている。
本レポートは以下の情報を提供する。
目次1.要旨
1.1.世界の商業・産業用蓄電池市場のヘッドラインとIDTechExの主要コメント
1.2.商業・産業用蓄電池市場における主要推進要因と機会
1.3.商業・産業用蓄電池市場における主要課題
1.4.商業・産業用蓄電池の概要
1.5.商業用・産業用蓄電池アプリケーションの概要
1.6.商業・産業用BESSのアプリケーション別展望 2026-2036年
1.7.主要なC&I BESS市場のヘッドライン 2025年
1.8.商業・産業用蓄電池のプレイヤーマップ
1.9.データセンター向け蓄電池の主要動向
1.10.データセンター向け蓄電池の代替技術(1)
1.11.データセンター向け蓄電池の代替技術(2)
1.12.データセンター向け蓄電池技術のタイプの変化
1.13.データセンター向け蓄電池市場の主な動向
1.14.通信基地局向けの代表的なリチウムイオン技術と動向
1.15.EV急速充電器用C&I電池
1.16.建設、農業、鉱業向けC&I BESSの概要
1.17.工場、病院、コミュニティ、ホテル、災害救援など、その他のC&I BESSアプリケーションの概要
1.18.商業用・産業用蓄電池の技術別需要比率 2025-2036年
1.19.商業・産業用蓄電池技術のベンチマーク、利点と欠点
1.20.商業・産業用途のリチウムイオンBESSコスト - 高出力対高エネルギー、2025年対2036年分析
1.21.世界の商業・産業用蓄電池の用途別需要予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
1.22.商業用・産業用蓄電池の世界地域別需要予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
1.23.商業用・産業用蓄電池の用途別世界市場規模予測 2025-2036年 (US$B)
1.24.商業用・産業用蓄電池の世界市場地域別金額予測 2025-2036年 (US$B)
2.商業用・産業用蓄電池の用途
2.1.商業・産業用蓄電池の概要
2.1.1.中核となる3つの BESS 市場セグメント
2.1.2.商業用・産業用蓄電池の紹介
2.1.3.商業用・産業用蓄電池アプリケーションの概要
2.1.4.BTMのまとめ:蓄電池が提供する価値-顧客側
2.2.データセンター向け蓄電池
2.2.1.要旨:データセンター向け蓄電池の主要動向
2.2.2.データセンター向け蓄電池の紹介
2.2.3.無停電電源装置の概要
2.2.4.無停電電源装置 - 用途の概要
2.2.5.データセンターの重要負荷と蓄電池への影響
2.2.6.3 種類の UPS システム(1)
2.2.7.3種類のUPSシステム(2)
2.2.8.無停電電源装置の例 - Riello UPS と Itility
2.2.9.無停電電源装置用ディーゼル発電機
2.2.10.無停電電源装置 - ディーゼル発電機からの置き換え
2.2.11.データセンターのダウンタイムのコスト
2.2.12.データセンターにおける C&I BESS の費用便益と投資回収時間
2.2.13.データセンターにおける蓄電池によるグリッドの柔軟性と費用対効果の改善
2.2.14.データセンターにおける代替蓄電池技術(1)
2.2.15.データセンター向け蓄電池の代替技術(2)
2.2.16.データセンターにおける蓄電池へのVertiv社からの期待
2.2.17.停電後の電力網供給とデータセンターへの負荷需要の問題
2.2.18.TerraFlow Energy - データセンター用フロー電池とLDUPS (1)
2.2.19.テラフローエナジー - データセンターとLDUPS用フロー電池(2)
2.3.通信基地局用蓄電池
2.3.1.移動体通信入門
2.3.2.2.3.2. 2Gから6Gまでのスペクトラム特性と予想される動向
2.3.3.6G - 主要アプリケーションの概要
2.3.4.無停電電源装置 - 電気通信の概要
2.3.5.通信基地局の代表的なリチウムイオン技術と動向
2.3.6.無停電電源装置 - 電気通信デジタル・アップグレード
2.3.7.無停電電源装置 - 米国における電気通信の法的要件
2.3.8.6G市場のさらなる調査
2.4.電気自動車充電インフラ用蓄電池
2.4.1.電気自動車の充電
2.4.2.EV急速充電器用C&I電池
2.4.3.電力会社側のアップグレードとサプライチェーンの制約によるDCFC導入の遅れ
2.4.4.グリッド接続なしの充電 - IaaS(インフラストラクチャー・アズ・ア・サービス)の開始
2.4.5.バッテリー統合型EV充電の仕組み
2.4.6.電気自動車充電インフラのさらなる研究
2.5.建設、農業、鉱業用蓄電池
2.5.1.建設・農業・鉱業用C&I BESSの概要
2.5.2.機械の電動化の利点/障壁
2.5.3.建設用電動車両の概要
2.5.4.農業用電動車両
2.5.5.その他の農業用車両
2.5.6.電動化を目指す主な鉱業用車両
2.5.7.電動CAM車の一般的なバッテリーパックサイズとC&I BESSの考慮点
2.5.8.建設、農業、鉱業における電気自動車と電気自動車用バッテリーに関するさらなる研究
2.6.その他の商業・産業用途の蓄電池
2.6.1.その他のC&I BESSアプリケーションの概要 - 工場、病院、コミュニティ、ホテル、災害救援など
2.6.2.マイクログリッド
2.6.3.マイクログリッド-利用動機と収益源
2.6.4.マイクログリッド-所有モデル
2.6.5.マイクログリッド - ケーススタディ
2.6.6.エネルギー使用時間の裁定取引
2.6.7.裁定取引の費用便益
3.商業・産業用蓄電池技術
3.1.蓄電池技術の概要
3.1.1.商業用・産業用蓄電池の技術別需要割合 % 2025-2036年
3.1.2.商業・産業用蓄電池技術に関する主な解説
3.1.3.商業・産業用蓄電池技術のベンチマーク、利点と欠点
3.2.リチウムイオン電池
3.2.1.種類以上のリチウムイオン電池
3.2.2.リチウムイオン電池の家系図
3.2.3.C&I BESS用リチウムイオン電池はLFPかNMCか?
3.2.4.C&IリチウムイオンBESS技術のベンチマークと分析
3.2.5.OBBBA:FEOC の制限、MACR の閾値、45X 生産クレジットの適格性への影響
3.2.6.OBBBA後の第48条投資税額控除(ITC)
3.2.7.2026年以降の中国産LFPセルと米国産LFPセルの最終コスト-関税導入と45X製造税額控除との比較分析(要約)
3.2.8.2026年以降の中国と米国のLFPセルの最終コスト-関税導入と45X製造税控除との比較分析(機会の窓)
3.2.9.2026 年以降の中国と米国の LFP セルの最終コスト - 関税導入と 45X 製造税額控除の比較分析 (OpexとCapex)
3.2.10.米国の電池用LFPセルと材料供給の現地化と第一次産業の対応
3.2.11.米国のESS用LFPセル製造工場(容量、プレーヤー、立地、状況別)
3.2.12.商業・産業用途のリチウムイオン BESS コスト - 高出力対高エネルギー、2025年対 2036年の分析
3.2.13.グリッド規模と住宅市場におけるリチウムイオン BESS のさらなる研究
3.3.レドックスフロー電池
3.3.1.レドックスフロー電池とリチウムイオン電池蓄電システムの比較 - GWh 別設置量、市場概要、主な利点
3.3.2.レドックスフロー電池の紹介
3.3.3.オールバナジウムRFB(VRFB)
3.3.4.VRFBの強みと弱み
3.3.5.アプリケーション別RFBプロジェクト2023-2025-C&I対グリッドスケールMWh
3.3.6.レドックスフロー電池のさらなる研究
3.4.電気自動車の二次電池
3.4.1.商業・産業用BESS用途のEV用二次電池(1)
3.4.2.商用・産業用BESS用途の電気自動車用二次電池(2)
3.4.3.電気自動車用二次電池のさらなる研究
3.5.Naイオン電池
3.5.1.Naイオン電池の紹介
3.5.2.Naイオンの評価(1)
3.5.3.Naイオンの評価(2)
3.5.4.定置用Naイオン電池
3.5.5.Naイオン電池のさらなる研究
3.6.鉛蓄電池
3.6.1.鉛蓄電池とバルブ制御鉛蓄電池(VRLA)
4.商業用・産業用蓄電池市場
4.1.商業・産業用BESSの用途別展望 2026-2036年
4.2.主要な C&I BESS 市場のヘッドライン 2025年
4.3.商業・産業用蓄電池のプレイヤーマップ
4.4.主要蓄電池データセンター市場の動向
4.5.TIAMAT - データセンター向けNaイオンBESSのターゲット
4.6.TIAMAT - データセンター用途の主要顧客と契約
4.7.データセンター支援のためのRFB - FlexBaseからのGWh規模のプロジェクト(1)
4.8.データセンター支援のためのRFB - FlexBaseからのGWh規模のプロジェクト(2)
4.9.XL Batteries - データセンター用フロー電池
4.10.TerraFlow Energy - データセンター及び LDUPS 用フロー電池(1)
4.11.TerraFlow Energy - データセンターおよびLDUPS用フロー電池(2)
4.12.電気通信基地局のバックアップ用EV用セカンドライフバッテリー
4.13.ハイスター - セルコスト、LFPとNaイオンの生産比較、通信用バックアップ電源用C&I電池
4.14.FEV - モバイル急速充電(MFC)ソリューション
4.15.E.ON - ドライブブースター
4.16.Jolt - MerlinOne(EV充電)
4.17.バッテリー・バッファによるEV充電プロジェクトのまとめ
4.18.BYD Super-eプラットフォームの発表
4.19.BESSによるMW充電のグリッド関連の課題の克服
4.20.BYD メガワット充電器
4.21.BYD の MW コネクタタイプ - MCS、ChaoJi、GB/T?
4.22.BYD の MW 充電用エネルギー貯蔵システム
4.23.Turntide Technologies - JCB のポータブル蓄電池用モジュール・サプライヤー
4.24.インドネシアの鉱業におけるC&I BESS
4.25.インドネシアの鉱業におけるC&I BESSとシュナイダーエレクトリックの洞察
4.26.シュナイダーエレクトリック - C&I BESS技術
4.27.シュナイダーエレクトリック - マイクログリッドと C&I BESS アプリケーション
4.28.シュナイダーエレクトリック - 主なマイクログリッド・プロジェクト
4.29.イートン株式会社 - C&I BESS
4.30.イートン社 - UPS 用 BESS
4.31.データセンター用サムスン第 3 世代リチウムイオン電池ラック
4.32.イートン株式会社 - ビジネスモデルと主要C&I BESSプロジェクト
4.33.Riello Elettronica - Riello UPS
4.34.Riello Elettronica - Riello Solartech
4.35.Riello UPS - 主要プロジェクト(1)
4.36.三菱電機 - C&I BESSとUPS (1)
4.37.三菱電機 - C&I BESS と UPS (2)
4.38.Saft - C&I BESS テクノロジー
4.39.Saft - 主要 C&I BESS プロジェクト
4.40.日本におけるCATLのC&I BESS活動
4.41.日本におけるCATLのBESS活動 - 技術の選択
4.42.テスラ - 主要グリッド規模発電事業者とC&I BESSプロジェクト
4.43.フルエンス - Smartstack BESS技術と日本市場参入計画
4.44.Fluence - Smartstack のエネルギー密度と市場平均との比較
4.45.ゴティオン - 世界の BESS 展開、コスト、C&I アプリケーションの主要動向
4.46.SolaX Power - C&I BESS と主要欧州ターゲット市場
4.47.AlphaESS - C&I BESS技術、ターゲット市場、顧客需要
4.48.Huawei FusionSolar ハイブリッド冷却によるC&I BESS技術
4.49.GivEnergy C&I BESS技術と主要アプリケーション
4.50.Growatt の概要 - モジュール式 C&I BESS 技術
4.51.Elite Battery Systems - C&I BESS モジュールとアプリケーション
4.52.東芝 - コンテナクレーン用LTOリチウムイオン電池(1)
4.53.東芝 - コンテナクレーン用LTOリチウムイオン電池(2)
4.54.住友電気工業 - VRFB、グローバルおよびC&I活動
4.55.出光興産 - 住友電工とオーストラリアでVRFBプロジェクト開発
4.56.セルキューブ - 新興 RFB 市場と主要アプリケーション
4.57.インヴィニティ・エナジー・システムズ - 主要市場の最新情報と議論
4.58.VFlowTech - シンガポールで誘導ポンプに電力を供給する VRFB 実証プロジェクト
4.59.TNO / ESS 社 - スキポール空港での全鉄 RFB プロジェクト
4.60.キノ・エナジー - 有機 RFB プロジェクトとアプリケーション
4.61.ジンクファイブ - Ni-Zn系BESS技術
4.62.ZincFive - 市場開発
4.63. Æsir Technologies - Ni-Zn 電池
4.64. Æsir Technologies - 市場開発
4.65.スタンダードエナジー - バナジウムイオン電池蓄電技術
4.66.スタンダードエナジー - 韓国におけるバナジウムイオン蓄電池の用途とBESS需要
4.67.蓄電池分野とエンドユーザー市場のさらなる調査
5.商業用・産業用蓄電池市場の予測 2025-2036年
5.1.商業用・産業用蓄電池市場の概要と対象予測
5.2.世界の商業用・産業用バッテリー蓄電市場のヘッドラインとIDTechExの主要コメント
5.3.市場予測の方法論と前提条件(1)
5.4.市場予測の方法論と前提条件(2)
5.5.商業用・産業用蓄電池の技術別需要割合 % 2025-2036年
5.6.商業用・産業用蓄電池の用途別世界需要予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
5.7.予測データ表:商業用・産業用蓄電池の用途別需要予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
5.8.商用・産業用蓄電池の世界地域別需要予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
5.9.予測データ表:商業用・産業用蓄電池の地域別需要予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
5.10.商業用・産業用蓄電池の用途別世界市場予測 2025-2036年 (US$B)
5.11.予測データ表:商業用・産業用蓄電池の用途別市場規模予測 2025-2036年 (US$B)
5.12.商業用・産業用蓄電池の世界市場地域別金額予測 2025-2036年 (US$B)
5.13.予測データ表商用・産業用蓄電池の地域別市場規模予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
5.14.中国の商業用・産業用蓄電池需要予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
5.15.予測データ表:中国の商業用および産業用蓄電池の需要予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
5.16.米国の商業用・産業用蓄電池需要予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
5.17.予測データ表:米国の商業用および産業用蓄電池の需要予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
5.18.欧州の商業用・産業用蓄電池需要予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
5.19.予測データ表:欧州の商業用および産業用蓄電池の需要 2025-2036年 (GWh)
5.20.欧州の商業用および産業用蓄電池需要予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
5.21.予測データ表:RoWの商業用および産業用蓄電池の需要予測 2025-2036年 (GWh)
5.22.データセンターの地域別蓄電池需要予測 2025-2036年 (GW)および蓄電期間(時間)
5.23.予測データ表:データセンターの蓄電池需要 2025-2036年 (GW)
6.企業プロファイル
6.1.アルファエス
6.2.ビープラネット・ファクトリー
6.3.BYD Energy Storage
6.4.CATL: Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
6.5.コネクテッド・エナジー
6.6.イートン・コーポレーション商業用・産業用バッテリー
6.7.エリート・バッテリー・システムズ
6.8.フレックスベース
6.9.フルエンス蓄電池システム(BESS)
6.10.ジブエナジー
6.11.ゴティオン
6.12.グローアット
6.13.H2, Inc.
6.14.ファーウェイ・フュージョンソーラー(BESS)
6.15.イマーサ
6.16.江蘇ハイスター電池製造
6.17.三菱電機C&I BESS & UPS
6.18.ナラダパワー
6.19.キノエナジー
6.20.リエロ・エレクトロニカRiello UPS と Riello Solartech
6.21.サフトC&I BESS と UPS
6.22.シュナイダーエレクトリック
6.23.スマートビル
6.24.ソラックスパワー
6.25.スタンダードエナジー(Vイオン電池)
6.26.住友電気工業
6.27.サンロー(BESS)
6.28.ティアマト・エナジー
6.29.ターンタイド・テクノロジーズ
6.30.VFlowTech
6.31.ゼノベー(Zenobē)
6.32.ジンクファイブC&I UPS
6.33. Æsir Technologies(旧ZAF Energy Systems):C&Iバッテリー
Summary
Granular 10-year forecasts on BESS for data centers and C&I applications. Analyses on players, key projects, applications, battery storage technology trends & benchmarking, LFP Li-ion costs & manufacturing. Insights from dozens of primary interviews.
Battery demand for stationary commercial and industrial (C&I) battery energy storage systems (BESS) is set to grow across a breadth of industries, including data centers, telecommunication base stations (5G, 6G), electric vehicle (EV) charging, construction, agriculture, mining, and other crucial applications such as factories, hospitals, communities, and disaster relief. Within these markets, C&I BESS is used in various applications, including uninterruptible power supply (UPS), peak shaving, microgrids, time-of-use arbitrage, grid flexibility, managing volatile artificial intelligence (AI) compute loads in data centers, among others. Across these industries, IDTechEx forecasts that by 2036, the global C&I BESS market will reach US$21B in value.

Overview of commercial and industrial battery storage applications. Source: IDTechEx.
C&I BESS Applications and Market Overview
The commercial and industrial (C&I) battery storage market has traditionally been viewed as a niche segment, especially in comparison to more established grid-scale and residential battery storage markets. However, this is set to change over the coming decade, with ~5x growth expected in C&I BESS demand between 2026 and 2036. Demand across applications will shift and transform over time, and C&I BESS players will have to adapt accordingly if they are to take their share of the market from incumbent Li-ion BESS giants such as CATL, BYD, and Tesla. This report provides insights from dozens of primary interviews with C&I BESS players, providing unique insights on projects, their targeted applications, and battery technologies.
In the short-term, BESS for data centers is set to become a rapidly growing application, especially in the US and Europe. Over time, global demand will shift in China to support the rollout of 6G. 5G (Sub-6 GHz) towers and 6G towers (will) see large macro towers being deployed. These could be considered critical nodes in the network backbone, and almost always have batteries for UPS / backup power, whether these are lead-acid or Li-ion, or even diesel generators to cover long outages. Towards the end of the next decade, the more significant uptake of EVs in agriculture and construction industries outside the US and Europe will drive C&I BESS to be deployed at these sites to support EV charging.
Battery Storage for Data Centers
Battery demand will closely follow the power demand of data centers, to at least cover their critical loads which includes servers, storage, and network gear. With the scale of hyperscale artificial intelligence (AI) data centers increasing, as will the power requirements and capacities of batteries for uninterruptible power supply (UPS). This will ensure data centers remain online, as per service level agreements, and prevent data loss, which could otherwise create large financial loss, pose security issues, and disruptions to key services.
One of the other key applications of battery storage in data centers will be to manage volatile AI compute loads. To counter these MW-scale swings in power demand, data center operators may run the data center at a higher continuous power by running extra operations, such that consistent power can be supplied from the electricity grid. However, this is a wasteful use of electricity which increases operating costs. Instead, and to reduce electricity costs, battery storage can be used to smoothen these fluctuations, by charging when there is excess electricity supply and discharging to the data center when power demand increases.

Fluctuating power demand from data center. Source: IDTechEx.
While valve-regulated lead acid (VRLA) batteries have traditionally been used in data centers for UPS, the higher cycle life and decreasing cost of Li-ion has seen these technologies steadily displacing VRLA batteries. However, key disadvantages of Li-ion batteries include their degradation, and safety risk due to flammable electrolyte. Frequent cycling per day could see their earlier retirement from data centers. Other battery storage technologies such as redox flow batteries (RFB) may be more suitable for managing volatile AI compute loads as they exhibit minimal degradation over extended cycling. RFBs also use non-flammable electrolyte, a key advantage considering the occurrence of Li-ion battery fires at data centers. Indeed, as the scale of data centers also increase, longer duration battery storage technologies, such as RFBs, may be needed as part of the wider energy management strategy for the data center facility. This report details key trends being observed for battery storage in data centers, including cost benefit analysis, use strategies, and future battery technology adoption.
Commercial and Industrial Battery Storage Technologies
Li-ion technology costs continue to decrease, and with the large surge in demand for data center BESS in the US and Europe, it will be important for domestic Li-ion supply chains to start being built up to reduce reliance on China. Through the 45X Manufacturing Production Tax Credit in the US, and via the One Big Beautiful Bill Act (OBBBA), the production of LFP Li-ion cells in the US will be key for supplying all domestic US Li-ion BESS markets, including commercial and industrial ones. This IDTechEx report provides developments in LFP manufacturing capacity in the US, and quantitative cost analysis on the costs of LFP cells manufactured in the US with the impact of tax credits compared to importing Chinese LFP cells with tariffs, from 2026 onwards.
Other than Li-ion, IDTechEx has observed Na-ion, VRLA, second-life EV, and redox flow batteries being developed for C&I applications. All technologies come with advantages and disadvantages related to cost, energy density, cycle life, safety, and response time. This report benchmarks these BESS technologies and discusses their suitability for C&I battery energy storage applications. Li-ion C&I BESS technologies from key manufacturers are benchmarked and C&I Li-ion BESS costs are provided by component breakdown.
Forecasts
This report includes granular 10-year market forecasts for global commercial and industrial BESS market, by GWh demand and market value (US$B) from 2025 to 2036, by application and by region. GWh forecasts by application per region are provided. Forecasts for BESS by GW in data centers are provided by region.
Company Profiles
This IDTechEx report includes 30+ company profiles, including C&I BESS players, major Li-ion BESS companies, and players developing alternative battery storage technologies, e.g., redox flow batteries, Na-ion, second-life EV, VRLA, and zinc-based batteries.
This report provides the following information
Table of Contents1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
1.1. Global commercial and industrial battery storage market headlines and IDTechEx key commentary
1.2. Key drivers and opportunities in the commercial and industrial battery storage market
1.3. Key challenges in the commercial and industrial battery storage market
1.4. Introduction to commercial and industrial battery storage
1.5. Overview of commercial and industrial battery storage applications
1.6. Commercial and industrial BESS outlook by application 2026 - 2036
1.7. Key C&I BESS market headlines 2025
1.8. Commercial and industrial battery storage player map
1.9. Key trends in battery storage for data centers
1.10. Alternative battery storage technologies for data centers (1)
1.11. Alternative battery storage technologies for data centers (2)
1.12. Shifts in type of battery storage technologies for data centers
1.13. Key battery storage data center market developments summary
1.14. Typical Li-ion technologies and trends for telecommunication base stations
1.15. C&I batteries for EV fast chargers
1.16. Overview of C&I BESS for construction, agriculture, and mining
1.17. Overview of other C&I BESS applications - factories, hospitals, communities, hotels, disaster relief, etc.
1.18. Commercial and industrial battery storage demand by technology split % 2025-2036
1.19. Commercial and industrial battery storage technology benchmarking, advantages and disadvantages
1.20. Li-ion BESS costs for commercial and industrial applications - high power vs high energy and 2025 vs 2036 analysis
1.21. Global commercial and industrial battery storage demand by application forecast 2025-2036 (GWh)
1.22. Global commercial and industrial battery storage demand by region forecast 2025-2036 (GWh)
1.23. Global commercial and industrial battery storage market value by application forecast 2025-2036 (US$B)
1.24. Global commercial and industrial battery storage market by region value forecast 2025-2036 (US$B)
2. COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL BATTERY STORAGE APPLICATIONS
2.1. Overview of commercial and industrial battery storage
2.1.1. The three core BESS market segments
2.1.2. Introduction to commercial and industrial battery storage
2.1.3. Overview of commercial and industrial battery storage applications
2.1.4. BTM summary: Values provided by battery storage - customer side
2.2. Battery storage for data centers
2.2.1. Executive summary: Key trends in battery storage for data centers
2.2.2. Introduction to battery storage for data centers
2.2.3. Introduction to uninterruptible power supply
2.2.4. Uninterruptible power supply - outline of uses
2.2.5. Critical load of data centers and impact on battery storage
2.2.6. Three types of UPS systems (1)
2.2.7. Three types of UPS systems (2)
2.2.8. Uninterruptible power supply example - Riello UPS and Itility
2.2.9. Diesel generators for uninterruptible power supply
2.2.10. Uninterruptible power supply - replacing diesel generators
2.2.11. Cost of data center downtime
2.2.12. Cost benefit and payback time for C&I BESS at data centers
2.2.13. Battery storage at data centers for grid flexibility and improving cost effectiveness
2.2.14. Alternative battery storage technologies for data centers (1)
2.2.15. Alternative battery storage technologies for data centers (2)
2.2.16. Expectations from Vertiv for battery storage in data centers
2.2.17. Issues with electricity grid supply and load demand with data centers after outages
2.2.18. TerraFlow Energy - flow batteries for data centers and LDUPS (1)
2.2.19. TerraFlow Energy - flow batteries for data centers and LDUPS (2)
2.3. Battery storage for telecommunication base stations
2.3.1. Introduction to mobile communications
2.3.2. Spectrum characteristics from 2G to 6G and expected trends
2.3.3. 6G - key applications overview
2.3.4. Uninterruptible power supply - telecommunications overview
2.3.5. Typical Li-ion technologies and trends for telecommunication base stations
2.3.6. Uninterruptible power supply - telecommunications digital upgrade
2.3.7. Uninterruptible power supply - legal requirements for telecommunications in the US
2.3.8. Further research on 6G markets
2.4. Battery storage for EV charging infrastructure
2.4.1. Electric vehicle charging
2.4.2. C&I Batteries for EV fast chargers
2.4.3. Delays in DCFC deployment due to utility-side upgrades and supply-chain constraints
2.4.4. Charging without a grid connection - the launch of Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS)
2.4.5. How battery integrated EV charging works
2.4.6. Further research on electric vehicle charging infrastructure
2.5. Battery storage for construction, agriculture, and mining
2.5.1. Overview of C&I BESS for construction, agriculture, and mining
2.5.2. Advantages of / barriers to machine electrification
2.5.3. Overview of electric construction vehicles
2.5.4. Agriculture vehicles for electrification
2.5.5. Other agriculture vehicles
2.5.6. Key mining vehicle types for electrification
2.5.7. Common battery pack sizes in electric CAM vehicles and considerations for C&I BESS
2.5.8. Further research on electric vehicles and EV batteries in construction, agriculture, and mining
2.6. Battery storage for other commercial and industrial applications
2.6.1. Overview of other C&I BESS applications - factories, hospitals, communities, hotels, disaster relief, etc.
2.6.2. Microgrids
2.6.3. Microgrids - motivations for use and revenue streams
2.6.4. Microgrids - ownership models
2.6.5. Microgrids - case studies
2.6.6. Energy time-of-use arbitrage
2.6.7. Cost benefit of arbitrage
3. BATTERY STORAGE TECHNOLOGIES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS
3.1. Battery storage technologies summary
3.1.1. Commercial and industrial battery storage demand by technology split % 2025-2036
3.1.2. Key commentary on battery technologies for commercial and industrial battery storage
3.1.3. Commercial and industrial battery storage technology benchmarking, advantages and disadvantages
3.2. Li-ion batteries
3.2.1. More than one type of Li-ion battery
3.2.2. A family tree of Li-based batteries
3.2.3. LFP or NMC Li-ion batteries for C&I BESS?
3.2.4. C&I Li-ion BESS technology benchmarking and analysis
3.2.5. OBBBA: FEOC restrictions, MACR thresholds and impact on 45X Production Credit eligibility
3.2.6. Section 48 Investment Tax Credit (ITC) after The OBBBA
3.2.7. Final costs of LFP cells from China and the US in 2026 and beyond - analysis of tariff implementation vs 45X Manufacturing Tax Credit (summary)
3.2.8. Final costs of LFP cells from China and the US in 2026 and beyond - analysis of tariff implementation vs 45X Manufacturing Tax Credit (opportunity window)
3.2.9. Final costs of LFP cells from China and the US in 2026 and beyond - analysis of tariff implementation vs 45X Manufacturing Tax Credit (Opex and Capex)
3.2.10. US battery LFP cell and material supply localization & first industry response
3.2.11. US LFP cell manufacturing plants for ESS by capacity, player, location, and status
3.2.12. Li-ion BESS costs for commercial and industrial applications - high power vs high energy and 2025 vs 2036 analysis
3.2.13. Further research on Li-ion BESS in grid-scale and residential markets
3.3. Redox flow batteries
3.3.1. Redox flow batteries vs Li-ion battery energy storage systems - installation by GWh, market overview, and key advantages
3.3.2. Redox flow battery introduction
3.3.3. All vanadium RFB (VRFB)
3.3.4. VRFB strengths and weaknesses
3.3.5. RFB projects 2023-2025 by application - C&I vs grid-scale by MWh
3.3.6. Further research on redox flow batteries
3.4. Second-life electric vehicle batteries
3.4.1. Second-life EV batteries for commercial and industrial BESS applications (1)
3.4.2. Second-life EV batteries for commercial and industrial BESS applications (2)
3.4.3. Further research on second-life electric vehicle batteries
3.5. Na-ion batteries
3.5.1. Na-ion batteries introduction
3.5.2. Appraisal of Na-ion (1)
3.5.3. Appraisal of Na-ion (2)
3.5.4. Na-ion batteries for stationary battery storage
3.5.5. Further research on Na-ion batteries
3.6. Lead-acid batteries
3.6.1. Lead-acid batteries and valve regulated lead-acid batteries (VRLA)
4. COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL BATTERY STORAGE MARKET
4.1. Commercial and industrial BESS outlook by application 2026 - 2036
4.2. Key C&I BESS market headlines 2025
4.3. Commercial and industrial battery storage player map
4.4. Key battery storage data center market developments summary
4.5. TIAMAT - Targeting Na-ion BESS for data center applications
4.6. TIAMAT - Key customer and contract for data center applications
4.7. RFB for data center support - GWh-scale project from FlexBase (1)
4.8. RFB for data center support - GWh-scale project from FlexBase (2)
4.9. XL Batteries - flow batteries for data centers
4.10. TerraFlow Energy - flow batteries for data centers and LDUPS (1)
4.11. TerraFlow Energy - flow batteries for data centers and LDUPS (2)
4.12. Second-life EV batteries for telecom base station backup power
4.13. Highstar - cell costs, LFP vs Na-ion production, and C&I batteries for telecom backup power
4.14. FEV - Mobile Fast Charging (MFC) solution
4.15. E.ON - Drive Booster
4.16. Jolt - MerlinOne (EV Charging)
4.17. Summary of battery buffered EV charging projects
4.18. BYD Super-e platform announcement
4.19. Overcoming grid related challenges of MW charging with BESS
4.20. BYD megawatt charger
4.21. BYD MW connector type - MCS, ChaoJi, or GB/T?
4.22. BYD energy storage system for MW charging
4.23. Turntide Technologies - module supplier for JCB's portable battery storage
4.24. C&I BESS in Indonesia' mining industry
4.25. C&I BESS in Indonesia's mining industry and insights from Schneider Electric
4.26. Schneider Electric - C&I BESS technology
4.27. Schneider Electric - microgrids and C&I BESS applications
4.28. Schneider Electric - key microgrid projects
4.29. Eaton Corporation - C&I BESS
4.30. Eaton Corporation - BESS for UPS
4.31. Samsung Gen 3 Li-ion battery racks for data centers
4.32. Eaton Corporation - business model and key C&I BESS projects
4.33. Riello Elettronica - Riello UPS
4.34. Riello Elettronica - Riello Solartech
4.35. Riello UPS - key projects (1)
4.36. Mitsubishi Electric - C&I BESS and UPS (1)
4.37. Mitsubishi Electric - C&I BESS and UPS (2)
4.38. Saft - C&I BESS technologies
4.39. Saft - key C&I BESS projects
4.40. CATL C&I BESS activity in Japan
4.41. CATL BESS activity in Japan - choice of technology
4.42. Tesla - key grid-scale player and C&I BESS projects
4.43. Fluence - Smartstack BESS technology and plans to enter Japanese market
4.44. Fluence - Smartstack energy density compared to market average
4.45. Gotion - key trends in global BESS deployment, costs, and C&I applications
4.46. SolaX Power - C&I BESS and key European target markets
4.47. AlphaESS - C&I BESS technologies, target markets, and customer demand
4.48. Huawei FusionSolar C&I BESS technology with hybrid cooling
4.49. GivEnergy C&I cabinet BESS technology and key applications
4.50. Growatt overview - modular C&I BESS technology
4.51. Elite Battery Systems - C&I BESS modules and applications
4.52. Toshiba - LTO Li-ion batteries for power container cranes (1)
4.53. Toshiba - LTO Li-ion batteries for power container cranes (2)
4.54. Sumitomo Electric - VRFBs, global and C&I activity
4.55. Idemitsu Kosan - VRFB project development in Australia with Sumitomo Electric
4.56. CellCube - emerging RFB markets and key applications
4.57. Invinity Energy Systems - key market updates and discussion
4.58. VFlowTech - VRFB demonstration project to power inductive pumps in Singapore
4.59. TNO / ESS Inc. - All-iron RFB project at Schiphol Airport
4.60. Quino Energy - organic RFB projects and applications
4.61. ZincFive - Ni-Zn BESS technology
4.62. ZincFive - market developments
4.63. Æsir Technologies - Ni-Zn batteries
4.64. Æsir Technologies - market developments
4.65. Standard Energy - Vanadium-ion battery storage technology
4.66. Standard Energy - V-ion battery storage applications and demand for BESS in South Korea
4.67. Further research in battery storage sectors and end-user markets
5. COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL BATTERY STORAGE MARKET FORECASTS 2025-2036
5.1. Overview of the commercial and industrial battery storage markets and forecasts covered
5.2. Global commercial and industrial battery storage market headlines and IDTechEx key commentary
5.3. Market forecast methodology and assumptions (1)
5.4. Market forecast methodology and assumptions (2)
5.5. Commercial and industrial battery storage demand by technology split % 2025-2036
5.6. Global commercial and industrial battery storage demand by application forecast 2025-2036 (GWh)
5.7. Forecast data table: Commercial and industrial battery storage demand by application 2025-2036 (GWh)
5.8. Global commercial and industrial battery storage demand by region forecast 2025-2036 (GWh)
5.9. Forecast data table: Commercial and industrial battery storage demand by region 2025-2036 (GWh)
5.10. Global commercial and industrial battery storage market value by application forecast 2025-2036 (US$B)
5.11. Forecast data table: Commercial and industrial battery storage market value by application 2025-2036 (US$B)
5.12. Global commercial and industrial battery storage market by region value forecast 2025-2036 (US$B)
5.13. Forecast data table: Commercial and industrial battery storage market value by region 2025-2036 (GWh)
5.14. China commercial and industrial battery storage demand forecast 2025-2036 (GWh)
5.15. Forecast data table: China commercial and industrial battery storage demand 2025-2036 (GWh)
5.16. US commercial and industrial battery storage demand forecast 2025-2036 (GWh)
5.17. Forecast data table: US commercial and industrial battery storage demand 2025-2036 (GWh)
5.18. Europe commercial and industrial battery storage demand forecast 2025-2036 (GWh)
5.19. Forecast data table: Europe commercial and industrial battery storage demand 2025-2036 (GWh)
5.20. RoW commercial and industrial battery storage demand forecast 2025-2036 (GWh)
5.21. Forecast data table: RoW commercial and industrial battery storage demand 2025-2036 (GWh)
5.22. Battery storage demand for data centers by region 2025-2036 (GW) and duration of storage (hours)
5.23. Forecast data table: Data center battery storage demand 2025-2036 (GW)
6. COMPANY PROFILES
6.1. AlphaESS
6.2. BeePlanet Factory
6.3. BYD Energy Storage
6.4. CATL: Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
6.5. Connected Energy
6.6. Eaton Corporation: Commercial and Industrial Batteries
6.7. Elite Battery Systems
6.8. FlexBase
6.9. Fluence: Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
6.10. GivEnergy
6.11. Gotion
6.12. Growatt
6.13. H2, Inc.
6.14. Huawei FusionSolar (BESS)
6.15. Immersa
6.16. Jiangsu Highstar Battery Manufacturing
6.17. Mitsubishi Electric: C&I BESS & UPS
6.18. Narada Power
6.19. Quino Energy
6.20. Riello Elettronica: Riello UPS and Riello Solartech
6.21. Saft: C&I BESS and UPS
6.22. Schneider Electric
6.23. Smartville
6.24. SolaX Power
6.25. Standard Energy (V-ion Batteries)
6.26. Sumitomo Electric Industries
6.27. Sungrow (BESS)
6.28. Tiamat Energy
6.29. Turntide Technologies
6.30. VFlowTech
6.31. Zenobē
6.32. ZincFive: C&I UPS
6.33. Æsir Technologies (Formerly ZAF Energy Systems): C&I Batteries
ご注文は、お電話またはWEBから承ります。お見積もりの作成もお気軽にご相談ください。本レポートと同分野(エネルギー貯蔵)の最新刊レポートIDTechEx社の エネルギー、電池 - Energy, Batteries分野 での最新刊レポート
よくあるご質問IDTechEx社はどのような調査会社ですか?IDTechExはセンサ技術や3D印刷、電気自動車などの先端技術・材料市場を対象に広範かつ詳細な調査を行っています。データリソースはIDTechExの調査レポートおよび委託調査(個別調査)を取り扱う日... もっと見る 調査レポートの納品までの日数はどの程度ですか?在庫のあるものは速納となりますが、平均的には 3-4日と見て下さい。
注文の手続きはどのようになっていますか?1)お客様からの御問い合わせをいただきます。
お支払方法の方法はどのようになっていますか?納品と同時にデータリソース社よりお客様へ請求書(必要に応じて納品書も)を発送いたします。
データリソース社はどのような会社ですか?当社は、世界各国の主要調査会社・レポート出版社と提携し、世界各国の市場調査レポートや技術動向レポートなどを日本国内の企業・公官庁及び教育研究機関に提供しております。
|
|