新興メモリとストレージ技術2025-2035年:市場、動向、予測Emerging Memory and Storage Technology 2025-2035: Markets, Trends, Forecasts 10年間のきめ細かな予測と市場サイジングにより、AI、HPC、データセンター、クラウド、エッジ、IoT、組み込みアプリケーション向けのHBM、QLC SSD、次世代HDD(HAMR、MAMR)、新興メモリ(MRAM、RRAM、FeRAM、... もっと見る

サマリー
10年間のきめ細かな予測と市場サイジングにより、AI、HPC、データセンター、クラウド、エッジ、IoT、組み込みアプリケーション向けのHBM、QLC SSD、次世代HDD(HAMR、MAMR)、新興メモリ(MRAM、RRAM、FeRAM、PCM)の進歩を網羅しています。
AIとHPCワークロードの爆発的な増加、データセンターとクラウドストレージの需要の高まり、IoTとエッジコンピューティングの拡大が、次世代メモリとストレージソリューションの必要性と新興メモリ技術の採用を促進している。IDTechExの調査レポート「新興メモリとストレージ技術2025-2035年」:市場、動向、予測」では、SSD(SLC、TLC、QLC)、HDD、磁気抵抗RAM(MRAM)、抵抗RAM(ReRAM/RRAM)、強誘電体RAM(FeRAM)、相変化メモリ(PCM)などの新興メモリソリューションなど、メモリとストレージの将来を形作る主要技術について考察している。また、現在の市場動向と新たな市場動向を分析し、各技術の展望を示し、新たな商機を浮き彫りにしています。ハードドライブディスク市場(HDD)の10年間の市場規模予測(用途別データセンター/クラウド、エッジアプリケーション)。
本レポートでカバーする主な市場予測:
メモリとストレージの主要動向
現在のメモリとストレージ市場は、3つの主要技術によって構築されている:HDD、SSD、DRAMである。SSDは、その高性能と低レイテンシにより、多くのアプリケーションでHDDに取って代わりつつある。しかし、大容量ストレージには依然としてHDDが不可欠である。クアッドレベル・セル(QLC)SSDの登場はストレージ階層を再構築し、速度と耐久性でHDDを上回ると同時に、あらゆるSSDの中で最も高い密度を提供します。
AIやHPCのワークロードがより高いパフォーマンスを要求する中、従来の階層型ストレージ(ホットデータ用にTLC SSD、コールドデータ用にHDD)からQLC SSDに切り替えることで、コストを大幅に削減できることが研究で示されています。10PB QLC SSDベースのストレージシステムでは、ラックスペース、消費電力、メンテナンスコストの削減により、10年間で3,030万米ドルのコスト削減が見込まれ、5年間で総所有コスト(TCO)が47%削減されると試算されています。このシフトは、高速で高密度のストレージに依存するAI、HPC、クラウドアプリケーションに特に関連している。
AI/HPCワークロードは、並列処理アプリケーションのために高い帯域幅を必要とするが、プロセッサの進歩がメモリ帯域幅を上回ることによって生じる、メモリの壁として知られるメモリボトルネックによる課題に直面している。例えば、生成AIで使用される大規模な言語モデル(LLM)は、このような制約により、プロセッサのピーク性能の50%未満になることがよくあります。データスループットを向上させるために、DRAMチップを垂直方向にスタックする高帯域幅メモリ(HBM)などのソリューションが採用されている。MRAMなどの新しい不揮発性メモリ(NVM)ソリューションも、ストレージクラスメモリ(SCM)アプリケーション向けに検討されています。
組み込みメモリ・アプリケーションでは、現在NORフラッシュが主流だが、性能、耐久性、スケーラビリティに限界がある。NORフラッシュは28nm以下の微細化に苦戦しており、マイクロコントローラ(MCU)製造用の先端CMOSプロセスとは互換性がありません。このため、ReRAMやMRAMのような、10nm以下の微細化が可能な新興のNVMソリューションにチャンスがもたらされています。Everspinのような企業はすでにこの分野で牽引力を得ており、TSMC、GlobalFoundries、Samsungなどの大手企業は新興NVMを自社のプラットフォームに統合しています。
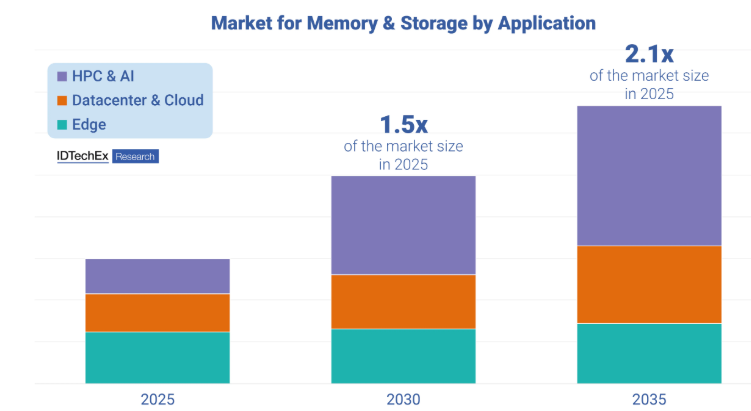
IDTechExのレポート「新興メモリとストレージ技術 2025-2035年」は次のように述べている:Markets,Trends,Forecasts "では、メモリとストレージ技術の市場規模は倍増し、新興メモリ技術はこの期間に現在の2.2倍に成長すると予測している。
主要トレンド、新興技術、市場見通しなど、進化するメモリとストレージの状況を理解したい方にとって、IDTechExのレポートは業界の将来についての詳細な評価を提供します。AI/HPC、クラウドストレージ、エッジコンピューティングの成長により、大容量・高性能ストレージや低消費電力の次世代・新興メモリソリューションへの需要が高まっている。
そのため、「新興メモリとストレージ技術 2025-2035年:Markets、Trends、Forecasts」は、メモリ・ストレージ市場全体だけでなく、HDD、SSD、DRAMなどの主要ハードウェア技術や主要アプリケーション分野についても包括的な10年予測を提供している。さらに、MRAM、ReRAM、FeRAM、PCMなどの主要技術をカバーする新興メモリ分野の予測も掲載しています。読者は、業界の現在と将来について深く理解し、十分な情報に基づいた戦略的意思決定を行うために必要な洞察力を身につけることができます。
主要な側面
本レポートは、現在のメモリおよびストレージ市場とその主要な応用分野に関する重要な市場情報を提供します。主要な商用技術に焦点を当てると同時に、新たなメモリおよびストレージソリューションとその現在および将来の用途を探求しています。内容は以下の通りです:
メモリ・ストレージ業界の背景と技術のレビュー
主要技術ごとの完全な市場特性:
包括的な市場分析:
目次
1.要旨
1.1データ増大とエネルギー消費の影響
1.2. 最新アプリケーションは高性能ストレージを要求している
1.3. 高性能ワークロードのメモリボトルネック
1.4. コンピューティングメモリの 階層構造
1.5.どのように機能するのか
1.6. 2024年のハードディスク・ドライブ市場
1.7. アプリケーション別ハードディスクドライブの予測
1.8. SSDのセル種類
1.9. SSDの主要メーカーと市場規模
1.10. QLC SSD & HDDの容量の変遷
1.11. QLC SSD & HDDの容量密度比較
1.12. QLC SSD & HDDの主要指標比較表
1.13. 予測:SSDとNANDのアプリケーション別市場動向
1.14. DRAMとは?
1.15. HBM
1.16. 予測:高帯域幅メモリ(HBM)の年間販売台数と市場規模
1.17. 予測: 新興メモリ技術
1.18. 新興のメモリ技術:PCRAM、FRAM、RRAM、MRAM
1.19. 新興不揮発性メモリ技術
1.20. 新興メモリ分野に関わる企業
1.21. 新興メモリは組み込み型ルートを取る
1.22. 新興メモリはストレージクラスメモリとしてまだ実現可能な道筋がある
1.23. 予測: IDTechExの分析:IDTechEx分析:MRAMの将来展望
1.24. IDTechExの洞察:MRAMの将来展望
1.25. IDTechExの洞察:FeRAMの将来展望
1.26. IDTechExの洞察:商業用FeRAMはHfO₂を採用しニッチ市場から脱却すべき
1.27. IDTechExの洞察:FeRAM
1.28. Failureof PCM as Storage Class Memory (2015-2023)
1.29. IDTechEx Outlook & Comments for PCM
1.30. Access More With an IDTechEx Subscription
2. はじめに
2.1.1. 一般計算におけるメモリ階層の理解
2.1.2. 現在の技術動向におけるストレージとメモリの動向
2.2. AI & HPC
2.2.1.HPC - 概要
2.2.2. AIがメモリソリューションの主要な推進力として機能
2.2.3. AIワークロードのためのクラスタにおけるストレージ階層を介したデータ移動
2.2.4. 現代のアプリケーションは高性能ストレージを要求している
2.2.5. HPCチップ統合のトレンドの概要
2.3. クラウドストレージ
2.3.1. データ増加とエネルギー消費の影響
2.3.2. データストレージのコスト 上昇
2.3.3.オンプレミス・クラウド・およびハイブリッドストレージソリューション:クラウドとハイブリッドへの移行
2.4. 組み込みメモリ
2.4.1. 組み込みメモリと組み込みシステムとは?
2.4.2. 組み込みメモリの種類
2.4.3. 組み込みフラッシュ、サブ 28nm で苦戦
2.4.4. 組み込みメモリを高度なノードに拡張することが重要な指標
2.5. エッジ・デバイスと IoT
2.5.1. エッジとクラウドの特徴
2.5.3. 自動車における組み込みメモリ
2.5.4. スマート家電におけるエッジAI
3. 予測
3.1. 予測手法
3.2. 予測: 用途別ハードディスク市場規模
3.3. 予測:SSDとNANDの用途別市場規模
3.4. 予測: 予測:ストレージ・クラウド/データセンターの市場規模
3.5. 予測:ストレージエッジ市場の市場規模
3.6. 予測:アプリケーション別メモリ
3.7. 予測:高帯域幅メモリ(HBM)の年間販売台数と市場規模
3.8. 予測:AI/HPC 向けサーバー用メモリとストレージ
3.9. 予測: 予測:用途別・タイプ別メモリ&ストレージ市場
3.10. 予測:トップレベル予測 メモリ&ストレージ市場
3.11. 予測: 新興メモリ市場の規模(種類別)
4. ストレージ
4.1. 概要
4.1.1. データ増大とエネルギー消費の影響
4.1.2. データストレージのコスト 上昇
4.1.3. 高性能を求める最新アプリケーション
4.1.4. 今日の技術環境におけるストレージの動向
4.1.5. データセンターにおけるストレージ
4.1.7. フラッシュストレージはHPCとAIアプリケーションの主要なストレージ技術である
4.1.8. HPCとAIは大規模で高性能なデータストレージを必要とする
4.1.9. AIワークロードによってストレージ要件は異なる
4.1.10. AIおよびHPCワークロード向けのSSD構成とソリューションの例
4.1.12. AIおよびデータセンター向けSK Hynix NANDフラッシュストレージの例
4.1.13. Solidigm(SK Hynixの子会社)は以前Intelが製造していたSSDを提供している
4.1.14. MicronはデータセンターとAI向けの多様なSSD製品群を提供している
4.1.15. Micron's 9550 SSDはPCel Gen5対応でAIの重要なワークロード向けに設計されている
4.1.16. KIOXIAはデータセンターとエンタープライズ向けのSSDソリューションを幅広く提供している
4.1.17. エッジコンピューティングデバイスにお超えるストレージ
4.2. ハードドライブディスク (HDDs)
4.2.1. HDDとは?どのように機能するのか
4.2.2. HDD技術の進歩
4.2.3. エネルギー補助磁気記録(EAMR)技術
4.2.4. データセンターHDDのマッチアップ
4.2.5. QLC SSDに対するHDDの利点と欠点
4.2.6. 2024年のハードディスク・ドライブ市場
4.2.7. HDD市場の歴史
4.3. ソリッド・ステート・ドライブ(SSD)
4.3.1.どのように機能するのか
4.3.2. NANDフラッシュメモリはフローティングゲートまたはチャージトラップを使用してデータを保存する
4.3.3. SSD技術の進歩
4.3.4. NAND層の積層
4.3.5. SKハイニックス - NAND技術開発
4.3.6. SKハイニックス: KIOXIA
4.3.7. KIOXIA はBiCS 3D FLASHTM技術を採用しストレージ密度を向上させている
4.3.8. SSDs Cell Types
4.3.9. SLC SSDs
4.3.10. ストレージクラスメモリ用のSSDが揮発性メモリとのギャップを埋める
4.3.11. TLC SSD
4.3.12. QLC SSD
4.3.13. 新興の低コストQLC NANDによるSSD容量の増加
4.3.14. QLCはビットあたりのコストを抑えながら大容量化を実現するが、性能面では不利
4.3.15. QLC SSD の利点と欠点
4.3.16. HDDとQLC SSDの使用例
4.3.17. EDSFF に移行するデータセンターとエンタープライズ SSD のフォームファクター
4.3.18. PCIe の各世代におけるシーケンシャルリード帯域幅の段階的変化
4.3.19. SSD市場におけるPCIe世代の進化
4.3.20. SSDの主要メーカーと市場規模
4.3.21. SSD市場の歴史的変遷
4.3.22. ストレージ市場
4.4. データベース比較 - QLC SSD & HDD
4.4.1. QLC SSD と HDD を比較する理由
4.4.2. 比較のための重要な KPI
4.4.3. QLC SSD と HDD の容量の進化
4.4.4. QLC SSD と HDD の容量密度の比較
4.4.5. QLC SSD と HDD のシーケンシャル帯域幅
4.4.6. QLC SSD と HDD の容量消費電力比
4.4.7. QLC SSD と HDD の容量密度 / 消費電力
4.4.8. QLC SSD と HDD の容量密度 / 消費電力
4.4.9. QLC SSD と HDD のベスト指標比較表
4.5.SK Hynix、2024年にペンタレベルの3D NANDフラッシュメモリを発表
4.5.1. SKハイニックスは2024年に5層構造の3D NANDフラッシュメモリを発表
4.5.2. Macronixは2024年にAIアプリケーション向けのCompute-In-Memory 3D NORフラッシュ技術を発表
4.5.3. SK HynixがLLM推論向け「アクセラレーター・イン・メモリ」を2024年に発表
5. MEMORY
5.1. 概要
5.1.1. 計算メモリの階層構造
5.1.2. HPC/AIワークロードにおけるメモリのボトルネックとプロセッサの未活用5.1.3. DRAMとは
5.1.4. SRAMとは
5.1.5. DRAM の種類と HBM と DDR の比較
5.1.6. コンピューティングにおける HBM対 DDR - 市場動向
5.2. DDR メモリ
5.2.1. ダブルデータレート(DDR)メモリの開発
5.2.2. HPC ワークロード向け AMD 第 4 世代 EPYC プロセッサにおける DDR5 メモリ
5.2.3. DDR5 MRDIMM が大容量と帯域幅を拡大し、CPU コア数を増加
5.2.4. NVIDIA の Grace CPU が LPDDR5X メモリを採用し、消費電力を低減
5.2.5. HPC および AI アプリケーションをターゲットとする主要企業がGDDR7を発表
5.2.6. GDDR6 と GDDR7 モジュールの比較
5.3. 高帯域幅メモリ(HBM)
5.3.1. HBM
5.3.2. 高帯域幅メモリ(HBM)と他のDRAM技術との比較
5.3.3. 2024 年には HBM の需要が供給を上回る
5.3.4. HBM(High Bandwidth Memory) パッケージング
5.3.5. HBMパッケージングのハイブリッドボンディングへの移行
5.3.6. μ バンプとハイブリッドボンディングを利用した HBM 性能のベンチマーク
5.3.7. SK Hynixが12層HBM3Eの量産を開始
5.3.8. MicronがNVIDIA H200向けに24GB HBM3Eをリリースし、36GB HBM3Eをサンプリング中
5.3.9. Samsungが2024年内にHBM3E 36GBの生産を見込んでいる
5.3.10. 主要3社による現在のHBM積層技術の概要
5.3.11. HBM世代の進化とHBM4への移行
5.3.12. 主要プレイヤーによる市場におけるHBM技術のベンチマーク(1)
5.3.13. 主要プレイヤーによる市場におけるHBM技術のベンチマーク(2)
5.3.14. HBMを使用するCPUおよびアクセラレータの例
5.3.15. インテルのHPCワークロード向けCPU Maxシリーズは、HBMとオプションのDDRを搭載
5.3.16. AMD CDNA 3 APU アーキテクチャにHPC向け統合型HBMメモリを搭載
5.3.17. HBMとGPUをパッケージ化する3つの主なアプローチ
5.3.18. 高帯域幅メモリ(HBM)の欠点
5.4. メモリ拡張
5.4.1. サムスンのAIおよびデータセンター・サーバー・アプリケーション向けCMM-Dメモリ拡張
5.4.2.マイクロンのデータセンターにおけるストレージ階層化向けのCXLメモリ拡5.4.3. メモリ市場
5.4.4. DDRメモリがCPUを支配する一方、HBMはGPU性能の鍵
5.5. メモリ市場
5.5.1. DDRメモリがCPUを支配する一方、HBMはGPU性能の鍵
5.5.2. メモリ市場
6. 概要
6.1.1. HPC/AIワークロードのメモリボトルネックとプロセッサの低稼働率
6.1.2. 組み込みフラッシュ、サブ28nmで苦戦
6.1.3. 組み込みメモリを高度なノードに拡張することは、主要指標にとって重要
6.1.4. メモリ技術の統合:PCRAM、FRAM、RRAM、MRAM
6.2. 磁気抵抗RAM(MRAM)
6.2.1. 磁気抵抗RAM(MRAM)とは?どのように機能するのか
6.2.2. (MRAM)の種類
6.2.3. MRAMの利点と欠点
6.2.4. MRAMの現在の用途
6.2.5. MRAMの特定企業と新興企業
6.2.6. MRAMの特定企業と新興企業
6.2.7. Everspin TechnologiesはディスクリートMRAMコンポーネントの主要サプライヤー
6.2.8. Everspin xSPI STT-MRAM、MRAMの新たなベンチマークを設定
6.2.9. Everspin・エッジAIおよび組み込みシステム向けにMRAMポートフォリオを拡大
6.2.10. Everspin・新たな用途でターゲット市場を拡大
6.2.11. Avalanche Technologyの航空宇宙用途でのMRAM採用
6.2.12. TSMCのMRAMへの関与
6.2.13. 自動車産業におけるTSMCとNXPのMRAM
6.2.14. TSMC: AIエッジデバイス向けにSTT-MRAMを共同最適化
6.2.15. MRAM研究開発におけるサムスンの役割
6.2.16. サムスン、車載アプリケーション向けに世界最書き込みエネルギー14nm eMRAM技術を発表
6.2.17. Netsol社・サムスンファウンドリーの28nmプロセスでMRAM製品を生産
6.2.18. Netsol社はサムスンのファウンドリ28nmプロセスを採用しMRAM製品を製造
6.2.19. Kioxia社、64GbクロスポイントMRAM向けに世界最小の1セレクタ-1MTJセルを発表
6.2.20. MRAM市場:企業タイプ別のセグメンテーション
6.2.21. IDTechEx分析 MRAMの将来展望
6.3. 抵抗変化型RAM(ReRAM)
6.3.1. 抵抗変化型RAM(ReRAM)とは?どのように機能するのか
6.3.2. ReRAMの利点と欠点
6.3.3. ReRAMの現在の用途
6.3.4. ReRAM市場:企業タイプ別のセグメンテーション
6.3.5. ReRAM市場の歴史的変遷
6.3.6. ReRAM特定企業と新興企業
6.3.7. ReRAM特定企業と新興企業
6.3.8. Weebit Nano社、AIアプリケーションにおけるReRAMのロードマップ
6.3.10. CrossBar Inc社、ReRAM技術をライセンス供与
6.3.11. CrossBar Inc、高性能組み込み型および 3D 高密度 ReRAM を提供
6.3.12. 4DS Memory、エリアベースのインターフェイススイッチング ReRAM を開発
6.3.13. RAMXEED ReRAM の技術と開発
6.3.14. GlobalFoundries社、22FDXプラットフォームでReRAMを実証
6.3.15. TSMC社、22nmのnRF54LシリーズSoCにReRAMを統合
6.3.16. IDTechEx分析
6.4. 強誘電体RAM(FeRAM)
6.4.1. 強誘電体RAM(FeRAM)とは?どのように機能するのか?
6.4.2. FeRAMの利点と欠点
6.4.3. FeRAMの現在の用途
6.4.4. FeRAM市場:企業タイプ別のセグメンテーション
6.4.5. RAMXEED FeRAMの技術と開発
6.4.6. インフィニオンはFeRAMの主要サプライヤー
6.4.7. Micron FeRAMが業界トップの密度を達成
6.4.8. 強誘電体メモリ会社、HfO2 FeRAM の商品化を目指す
6.4.9. SK ハイニックス、超高密度 3D FeNAND アレイを発表、ハイパースケール AI モデルのアナログ演算に対応
6.4.10. TSMC 最小のセル面積と高い耐久性を備えたフェロエレクトリックFETメモリを展示
6.4.11. IDTechEx インサイト - 商業用FeRAMは競争力を維持するためにHfO₂が必要
6.4.12. IDTechEx展望とコメント FeRAM
6.5. 相変化メモリ(PCM)
6.5.1. フェーズチェンジメモリ(PCM/PCRAM)とはなにか、どのように機能するか
6.5.2. PCMの利点と欠点
6.5.3. PCM市場:企業タイプ別のセグメンテーション
6.5.4. PCM市場 Intel Optaneの失敗からの教訓
6.5.5. Micron 3DX ポイント
6.5.6. ストレージクラスメモリとしてのPCMの 失敗(2015-2023年)
6.5.7. STMicroelectronicsは車載コントローラのマイクロコントローラ向けにePCMを製造
6.5.8. STMicroelectronicsはエッジ AI アプリケーションにおけるニュートラルネットワークの重み保存用に単一端子のePCMメモリアレイを提案
6.5.9. PCM 市場
6.5.10. IDTechEx展望とコメント PCM
6.6.エマージングメモリはストレージクラスメモリとしてまだ実現可能な道筋がある
6.6.2. エマージングメモリは組み込み路線をとる
6.6.3. エマージング技術の比較
6.6.4. IDTechExによる商業化された新興技術製品の比較
6.6.5. 新興メモリー分野に関わる企業
7. COMPANY PROFILES
7.1. 本レポートに含まれる企業プロファイル
Summary
10-year granular forecast and market sizing, this report covers advancements in HBM, QLC SSDs, next-gen HDDs (HAMR, MAMR), and emerging memory (MRAM, RRAM, FeRAM, PCM) for AI, HPC, data centers, cloud, edge, IoT, and embedded applications.
The explosion of AI and HPC workloads, the rising demand for data centers and cloud storage, and the expansion of IoT and edge computing are driving the need for next-generation memory and storage solutions, as well as the adoption of emerging memory technologies. IDTechEx's report, "Emerging Memory and Storage Technology 2025-2035: Markets, Trends, Forecasts", examines key technologies shaping the future of memory and storage, including SSDs (SLC, TLC, and QLC), HDDs, and emerging memory solutions such as Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM), Resistive RAM (ReRAM/RRAM), Ferroelectric RAM (FeRAM), and Phase-Change Memory (PCM). The report also analyzes current and emerging market trends, provides an outlook for each technology, and highlights new commercial opportunities. A 10-year market size forecast for Hard Drive Disk Market (HDD), segmented by Application Datacentres/Cloud and Edge Applications.
Key Market Forecasts Covered in the Report:
Key Trends in Memory and Storage
The current memory and storage market is built on three dominant technologies: HDDs, SSDs, and DRAM. SSDs are increasingly replacing HDDs in many applications due to their higher performance and lower latency. However, HDDs remain essential for high-capacity storage. The introduction of Quad-Level Cell (QLC) SSDs is reshaping storage hierarchies, offering the highest density of any SSD while outperforming HDDs in speed and endurance.
As AI and HPC workloads demand greater performance, studies show that switching from traditional tiered storage (TLC SSDs for hot data and HDDs for cold data) to QLC SSDs can significantly reduce costs. A 10PB QLC SSD-based storage system is estimated to provide US$30.3 million in savings over 10 years, with a 47% reduction in total cost of ownership (TCO) over five years due to lower rack space, power consumption, and maintenance costs. This shift is particularly relevant for AI, HPC, and cloud applications, which rely on high-speed, high-density storage.
AI/HPC workloads require high bandwidth for parallel processing applications but face challenges due to memory bottlenecks—known as the memory wall—caused by processor advancements outpacing memory bandwidth. For example, large language models (LLMs) used in generative AI often experience less than 50% of peak processor performance due to these constraints. Solutions such as High Bandwidth Memory (HBM), which vertically stacks DRAM chips, are being adopted to increase data throughput. Emerging non-volatile memory (NVM) solutions, such as MRAM, are also being explored for storage-class memory (SCM) applications.
In embedded memory applications, NOR Flash currently dominates, but it faces limitations in performance, endurance, and scalability. NOR Flash struggles to scale below 28nm, making it incompatible with advanced CMOS processes for microcontroller (MCU) manufacturing. This has created an opportunity for emerging NVM solutions like ReRAM and MRAM, which can scale below 10nm. Companies like Everspin have already gained traction in this space, while major players such as TSMC, GlobalFoundries, and Samsung are integrating emerging NVM into their platforms.
IDTechEx's report "Emerging Memory and Storage Technology 2025-2035: Markets, Trends, Forecasts" projects that the market size for memory and storage technologies will double, with emerging memory technologies expected to grow 2.2 times their current size over this period.
 
For those looking to understand the evolving memory and storage landscape, including key trends, emerging technologies, and market outlooks, IDTechEx's report provides a detailed assessment of the industry's future. The growth of AI/HPC, cloud storage, and edge computing is driving demand for high-capacity, high-performance storage and low power, next-generation and emerging memory solutions.
As such, "Emerging Memory and Storage Technology 2025-2035: Markets, Trends, Forecasts" provides comprehensive 10-year forecasts not only for the overall memory and storage market but also for key hardware technologies, including HDDs, SSDs, and DRAM, as well as major application areas. In addition, it provides forecasts for the emerging memory sector, covering key technologies such as MRAM, ReRAM, FeRAM, and PCM. Readers will gain a deep understanding of the present and future of the industry, equipping them with the insights needed to make informed strategic decisions.
Key Aspects
This report provides critical market intelligence on the current memory and storage market and its key application sectors. It highlights the dominant commercial technologies while exploring emerging memory and storage solutions and their current and future applications. This includes:
A Review of the Context and Technology within the Memory & Storage Industry:
Full Market Characterization for Each Major Technology:
Comprehensive Market Analysis:
Table of Contents1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
1.1. The Impact of Data Growth and Energy Consumption
1.2. Modern Applications are Demanding High Performance Storage
1.3. Memory bottlenecks for High Performance workloads
1.4. Hierarchy of computing memory
1.5. What are HDDs? How Do They Work?
1.6. Hard Disk Drive Market in 2024
1.7. Forecast: Hard Disk Drive by Application
1.8. SSDs Cell Types
1.9. Key Manufactures of SSDs and Market Size
1.10. Evolution of Capacity in QLC SSDs & HDDs
1.11. Capacity Density Comparison of QLC SSDs & HDDs
1.12. QLC SSDs & HDDs Best Metric Comparison Table
1.13. Forecast: SSDs & NAND by Application
1.14. What is DRAM?
1.15. HBM
1.16. Forecast: Yearly Unit Sales and Market Size of High Bandwidth Memory (HBM)
1.17. Forecast: Memory by Application
1.18. Emerging memory technologies: PCRAM, FRAM, RRAM, MRAM.
1.19. Emerging Non-Volatile Memory Technology
1.20. Companies involved within the Emerging Memory Space
1.21. Emerging Memory is Taking the Embedded Route
1.22. Emerging Memory Still Has a Path to Viability as Storage-Class Memory
1.23. Forecast: Market size of Emerging Memory by Type
1.24. IDTechEx Analysis: Future Outlook for MRAM
1.25. IDTechEx Analysis: Future Outlook for ReRAM
1.26. IDTechEx insight: Commercial FeRAM should adopt HfO₂ to move out of niche
1.27. IDTechEx Outlook & Comments for FeRAM
1.28. Failure of PCM as Storage Class Memory (2015-2023)
1.29. IDTechEx Outlook & Comments for PCM
1.30. Memory and Storage Technology Readiness Level
1.31. Access More With an IDTechEx Subscription
2. INTRODUCTION
2.1.1. Understanding the Memory Hierarchy for General Computing
2.1.2. Trends for storage and memory in Todays tech climate
2.2. AI & HPC
2.2.1. HPC - overview
2.2.2. AI as a Leading Driver for Memory solutions
2.2.3. Data movement through storage tiers in clusters for AI workloads
2.2.4. Modern Applications are Demanding High Performance Storage
2.2.5. Memory bottlenecks for High Performance workloads
2.2.6. Overview of trends in HPC chip integration
2.3. Cloud Storage
2.3.1. The Impact of Data Growth and Energy Consumption
2.3.2. Rising Data Storage Costs
2.3.3. On-premises, cloud, and hybrid storage solutions: Shift towards cloud & hybrid
2.4. Embedded Memory
2.4.1. What are Embedded Memory and Embedded Systems?
2.4.2. Types of Embedded Memory
2.4.3. Embedded Flash Struggles with sub-28nm
2.4.4. Scaling Embedded Memory to Advanced Nodes is Important for Key Metrics
2.5. Edge Devices & IoT
2.5.1. Edge Devices also is a Driver for Memory Solutions
2.5.2. Edge vs Cloud characteristics
2.5.3. Embedded Memory in Automotive Vehicles
2.5.4. Edge AI in Smart Appliances
3. FORECASTS
3.1. Forecast Methodology
3.2. Forecast: Market size of Hard-Drive-Disk by Application
3.3. Forecast: SSDs & NAND by Application
3.4. Forecast: Market size of Storage Cloud/Data Center Market
3.5. Forecast: Market size of Storage Edge Market
3.6. Forecast: Memory by Application
3.7. Forecast: Yearly Unit Sales and Market Size of High Bandwidth Memory (HBM)
3.8. Forecasts: Memory and Storage for Servers for AI/HPC
3.9. Forecast: Memory & Storage Market by Application & Type
3.10. Forecast: Top Level Forecast Memory & Storage Market
3.11. Forecast: Market size of Emerging Memory by Type
4. STORAGE
4.1. Overview
4.1.1. The Impact of Data Growth and Energy Consumption
4.1.2. Rising Data Storage Costs
4.1.3. Modern Applications are Demanding High Performance
4.1.4. Trends for Storage in Todays Tech Climate
4.1.5. Understanding the Memory Hierarchy for General Computing
4.1.6. Storage in Datacentres
4.1.7. Flash storage is the leading storage technology for HPC and AI applications
4.1.8. HPC and AI require large-scale and high-performance data storage
4.1.9. Storage requirements varies depending on the AI workloads
4.1.10. Data movement through storage tiers in clusters for AI workloads
4.1.11. Example of SSD configurations and solutions for AI and HPC workloads
4.1.12. Examples of SK Hynix NAND Flash storage for AI and data centers
4.1.13. Solidigm (SK Hynix subsidiary) offers SSDs previously manufactured by Intel
4.1.14. Micron has a range of SSDs for applications in datacenters and AI
4.1.15. Micron's 9550 SSDs are designed for AI-critical workloads with PCIe Gen5
4.1.16. KIOXIA offers a range of datacenter and enterprise SSD solutions
4.1.17. Storage in Edge Computing Devices
4.2. Hard Drive Disks (HDDs)
4.2.1. What are HDDs? How Do They Work?
4.2.2. Advancements in HDD Technology
4.2.3. Energy-Assisted Magnetic Recording (EAMR) Technologies
4.2.4. Data Centre HDD match up
4.2.5. Benefits and Drawbacks to HDDs relative to QLC SSDs
4.2.6. Hard Disk Drive Market in 2024
4.2.7. HDDs Market Historically
4.3. Solid State Drives (SSDs)
4.3.1. What are SSDs? How Do They Work?
4.3.2. NAND Flash memory uses floating gates or charge traps to store data
4.3.3. Advancements in SSD Technology
4.3.4. NAND Layer Stacking
4.3.5. SK Hynix - NAND technology development
4.3.6. SK Hynix: Overcoming stacking limitations to increase capacity using 4D2.0
4.3.7. KIOXIA uses BiCS 3D FLASHTM Technology to increase storage density
4.3.8. SSDs Cell Types
4.3.9. SLC SSDs
4.3.10. SSDs for storage class memory bridging gap to volatile memory
4.3.11. TLC SSDs
4.3.12. QLC SSDs
4.3.13. Increasing SSD capacity through emerging lower cost QLC NAND
4.3.14. QLC affords higher capacity at a lower cost per bit but with performance deficits
4.3.15. Benefits and Drawbacks to QLC SSDs
4.3.16. Use Cases of HDDs & QLC SSDs
4.3.17. Data center and enterprise SSD form factors transitioning towards EDSFF
4.3.18. Step change in sequential read bandwidth with each generation of PCIe
4.3.19. Evolution of PCIe generations in the SSD market
4.3.20. Key Manufactures of SSDs and Market Size
4.3.21. SSD Market Historically
4.3.22. Storage Market
4.4. Database Comparison - QLC SSD & HDD
4.4.1. Why Compare QLC SSDs & HDDs
4.4.2. Important KPI's for Comparison
4.4.3. Evolution of Capacity of QLC SSDs & HDDs
4.4.4. Capacity Density Comparison of QLC SSDs & HDDs
4.4.5. Sequential Bandwidth of QLC SSDs & HDDs
4.4.6. Capacity-to-Power Ratio of QLC SSDs & HDDs
4.4.7. Capacity Density / Power of QLC SSDs & HDDs
4.4.8. Capacity Density / Power of QLC SSDs & HDDs
4.4.9. QLC SSDs & HDDs Best Metric Comparison Table
4.5. Going Forward - Improving Current Technologies
4.5.1. SK Hynix Unveils Penta-Level 3D NAND Flash Memory in 2024
4.5.2. Macronix Introduced Compute-In-Memory 3D NOR Flash technology for AI Applications in 2024
4.5.3. SK Hynix introduced Accelerator-in-Memory for LLM Inference
5. MEMORY
5.1. Overview
5.1.1. Hierarchy of computing memory
5.1.2. Memory bottlenecks for HPC/AI workloads and processor under-utilization
5.1.3. What is DRAM?
5.1.4. What is SRAM?
5.1.5. Types of DRAM and Comparison of HBM with DDR
5.1.6. HBM vs DDR for computing - market trend
5.2. DDR Memory
5.2.1. Developments in double data rate (DDR) memory
5.2.2. DDR5 memory in AMD's 4th Gen EPYC processors for HPC workloads
5.2.3. DDR5 MRDIMM increases capacity and bandwidth for high CPU core counts
5.2.4. NVIDIA's Grace CPU uses LPDDR5X memory to lower power consumption
5.2.5. GDDR7 announced by major players targeting HPC and AI applications
5.2.6. Comparison of GDDR6 and GDDR7 modules
5.3. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM)
5.3.1. HBM
5.3.2. High bandwidth memory (HBM) and comparison with other DRAM technologies
5.3.3. Demand outgrows supply for HBM in 2024
5.3.4. HBM (High Bandwidth Memory) packaging
5.3.5. HBM packaging transition to hybrid bonding
5.3.6. Benchmark of HBM performance utilizing µ bump and hybrid bonding
5.3.7. SK Hynix has started volume production of 12-layer HBM3E
5.3.8. Micron released 24GB HBM3E for NVIDIA H200 and is sampling 36GB HBM3E
5.3.9. Samsung expects production of HBM3E 36GB within 2024
5.3.10. Overview of current HBM stacking technologies by 3 main players
5.3.11. Evolution of HBM generations and transition to HBM4
5.3.12. Benchmarking of HBM technologies in the market from key players (1)
5.3.13. Benchmarking of HBM technologies in the market from key players (2)
5.3.14. Examples of CPUs and accelerators using HBM
5.3.15. Intel's CPU Max series for HPC workloads has HBM and optional DDR
5.3.16. AMD CDNA 3 APU architecture with unified HBM memory for HPC
5.3.17. Three main approaches to package HBM and GPU
5.3.18. Drawbacks of High Bandwidth Memory (HBM)
5.4. Memory Expansion
5.4.1. Samsung's CMM-D memory expansion for AI and datacenter server applications
5.4.2. Micron's CXL memory expansion modules for storage tiering in datacenters
5.4.3. Memory Market
5.4.4. DDR memory dominates CPUs whereas HBM is key to GPU performance
5.5. Memory Market
5.5.1. DDR memory dominates CPUs whereas HBM is key to GPU performance
5.5.2. Memory market
6. EMERGING STORAGE & MEMORY
6.1. Overview
6.1.1. Memory bottlenecks for HPC/AI workloads and processor under-utilization
6.1.2. Embedded Flash Struggles with sub-28nm
6.1.3. Scaling Embedded Memory to Advanced Nodes is Important for Key Metrics
6.1.4. Emerging memory technologies: PCRAM, FRAM, RRAM, MRAM.
6.2. Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM)
6.2.1. What is Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM)? How Does it Work?
6.2.2. Types of (MRAM)
6.2.3. Benefits and Drawbacks to MRAM
6.2.4. Current Applications of MRAM
6.2.5. MRAM Specific Companies & Startups
6.2.6. MRAM Specific Companies & Startups
6.2.7. Everspin Technologies is the leading supplier of discrete MRAM components
6.2.8. Everspin xSPI STT-MRAM sets new benchmark MRAM
6.2.9. Everspin Expands MRAM Portfolio for Edge AI and Embedded Systems
6.2.10. Everspin Target Markets is Growing With New applications
6.2.11. Avalanche Technology's MRAM Adoption in Aerospace Applications
6.2.12. TSMC's Involvement in MRAM
6.2.13. TSMC and NXP MRAM in Automotive Industry
6.2.14. TSMC: STT-MRAM Co-Optimized for AI Edge Devices
6.2.15. Samsung's Role in MRAM Research and Development
6.2.16. Samsung Unveils World Most Write Energy 14nm eMRAM Technology for Automotive Applications
6.2.17. Samsung Reveals Smallest-Cell eMRAM Compatible With 8nm Logic Node for Automotive Applications
6.2.18. Netsol Uses Samsung Foundry 28nm Process to produce MRAM Products
6.2.19. Kioxia Introduces World Smallest 1Selector-1MTJ Cell for 64 Gb Cross-Point MRAM
6.2.20. MRAM Market: Segmentation by Company Type
6.2.21. IDTechEx Analysis: Future Outlook for MRAM
6.3. Resistive RAM (ReRAM)
6.3.1. What is Resistive Ram (ReRAM)? How Does it Work?
6.3.2. Benefits and Drawbacks to ReRAM
6.3.3. Current Applications of ReRAM
6.3.4. ReRAM Market: Segmentation by Company Type
6.3.5. ReRAM Market Historically
6.3.6. ReRAM Specific Companies & Startups
6.3.7. ReRAM Specific Companies & Startups
6.3.8. Weebit Nano Developing and Licensing ReRAM Technology
6.3.9. Weebit Nano's Roadmap for ReRAM in AI Applications
6.3.10. CrossBar Inc Licensing ReRAM Technology
6.3.11. CrossBar Inc Provides High Performance Embedded and 3D High Density ReRAM
6.3.12. 4DS Memory Develops Area Based Interface Switching ReRAM
6.3.13. RAMXEED ReRAM Technology and Development
6.3.14. GlobalFoundries Demonstrates ReRAM in its 22FDX Platform
6.3.15. TSMC integrates ReRAM into its nRF54L Series SoCs AT 22nm
6.3.16. IDTechEx Analysis: Future Outlook for ReRAM
6.4. Ferroelectric RAM (FeRAM)
6.4.1. What is Ferroelectric RAM (FeRAM)? How Does it Work?
6.4.2. Benefits and Drawbacks to FeRAM
6.4.3. Current Applications of FeRAM
6.4.4. FeRAM Market: Segmentation by Company Type
6.4.5. RAMXEED FeRAM Technology and Development
6.4.6. Infineon is a leading supplier of FeRAM
6.4.7. Micron FeRAM Achieves Industry-Leading Density
6.4.8. Ferroelectric Memory Company Targets HfO2 FeRAM Commercialization
6.4.9. SK Hynix Unveils Ultra-High-Density 3D FeNAND Arrays for Analog Computation of Hyperscale AI Models
6.4.10. TSMC Showcases Ferroelectric FET Memory with Smallest Cell Area and High Endurance
6.4.11. IDTechEx Insight - Commercial FeRAM Needs HfO₂ to Stay Competitive
6.4.12. IDTechEx Outlook & Comments for FeRAM
6.5. Phase Change Memory (PCM)
6.5.1. What is Phase Change Memory (PCM/PCRAM) How Does it Work?
6.5.2. Benefits and Drawbacks to PCM
6.5.3. PCM Market: Segmentation by Company Type
6.5.4. PCM Market Lessons from Intel Optane Failure
6.5.5. Micron 3DXPoint
6.5.6. Failure of PCM as Storage Class Memory (2015-2023)
6.5.7. STMicroelectronics produces ePCM for Microcontrollers in automotive controllers
6.5.8. STMicroelectronics presents Single-Ended ePCM Memory Array for Neural Network Weight Storage in Edge-AI Applications
6.5.9. PCM Market
6.5.10. IDTechEx Outlook & Comments for PCM
6.6. Comparison of Emerging Memory Platforms
6.6.1. Emerging Memory Still Has a Path to Viability as Storage-Class Memory
6.6.2. Emerging Memory is Taking the Embedded Route
6.6.3. Comparison of Emerging Technology
6.6.4. IDTechEx Comparison of Commercialized Emerging Tech Products
6.6.5. Companies involved within the Emerging Memory Space
7. COMPANY PROFILES
7.1. Company Profiles Included with this Report
ご注文は、お電話またはWEBから承ります。お見積もりの作成もお気軽にご相談ください。本レポートと同分野(データセンタ)の最新刊レポート
IDTechEx社の 半導体、コンピュータ、AI - Semiconductors, Computing, AI分野 での最新刊レポート
関連レポート(キーワード「メモリ」)よくあるご質問IDTechEx社はどのような調査会社ですか?IDTechExはセンサ技術や3D印刷、電気自動車などの先端技術・材料市場を対象に広範かつ詳細な調査を行っています。データリソースはIDTechExの調査レポートおよび委託調査(個別調査)を取り扱う日... もっと見る 調査レポートの納品までの日数はどの程度ですか?在庫のあるものは速納となりますが、平均的には 3-4日と見て下さい。
注文の手続きはどのようになっていますか?1)お客様からの御問い合わせをいただきます。
お支払方法の方法はどのようになっていますか?納品と同時にデータリソース社よりお客様へ請求書(必要に応じて納品書も)を発送いたします。
データリソース社はどのような会社ですか?当社は、世界各国の主要調査会社・レポート出版社と提携し、世界各国の市場調査レポートや技術動向レポートなどを日本国内の企業・公官庁及び教育研究機関に提供しております。
|
|













