先進半導体パッケージング2025-2035年:予測、技術、用途Advanced Semiconductor Packaging 2025-2035: Forecasts, Technologies, Applications 半導体パッケージング技術の進化 半導体パッケージングは、従来の1次元PCB設計からウェハレベルでの最先端の3次元ハイブリッドボンディングへと進化してきた。この進歩により、高いエネルギー効率を維持... もっと見る

出版社
IDTechEx
アイディーテックエックス 出版年月
2024年10月17日
価格
お問い合わせください
ライセンス・価格情報/注文方法はこちら 納期
お問合わせください
ページ数
530
言語
英語
※ 調査会社の事情により、予告なしに価格が変更になる場合がございます。
サマリー
半導体パッケージング技術の進化
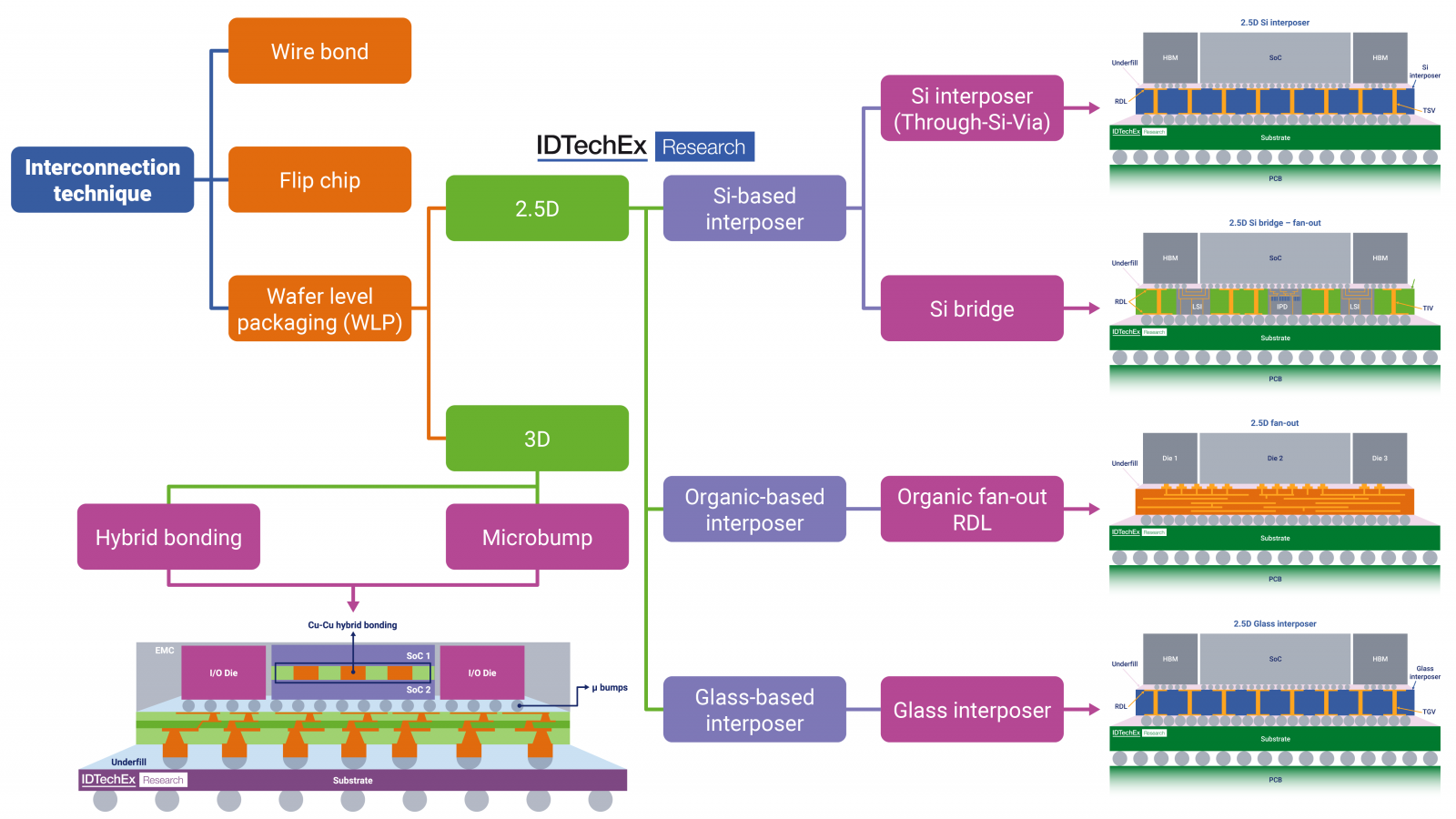
半導体パッケージングは、従来の1次元PCB設計からウェハレベルでの最先端の3次元ハイブリッドボンディングへと進化してきた。この進歩により、高いエネルギー効率を維持しながら、1桁マイクロメートル範囲の相互接続ピッチと最大1000GB/秒の帯域幅が可能になりました。最先端の半導体パッケージング技術の中心は、インターポーザー上でコンポーネントを並べて配置する2.5Dパッケージングと、アクティブダイを垂直に積み重ねる3Dパッケージングである。これらの技術は、将来のHPCシステムにとって極めて重要である。
2.5Dパッケージング技術にはさまざまなインターポーザー材料が使用され、それぞれに明確な利点と欠点があります。シリコン(Si)インターポーザは、完全なパッシブSiウェーハと局所的なSiブリッジを含み、微細な配線機能を容易にすることで知られ、高性能コンピューティングに理想的です。しかし、材料費と製造コストが高く、実装面積にも限界があります。このような問題を軽減するため、微細配線が必要な箇所でシリコンを戦略的に利用し、面積の制約に対応するローカライズドSiブリッジの利用が増加している。
有機インターポーザは、ファンアウト成形コンパウンドを使用し、シリコンに代わるよりコスト効率の高い選択肢を提供します。有機インターポーザは誘電率が低いため、パッケージ内のRC遅延が減少します。このような利点があるにもかかわらず、有機インターポーザはシリコンベースのパッケージと同レベルのインターコネクト機能削減を達成するのに苦労しており、高性能コンピューティング・アプリケーションでの採用が制限されています。
ガラス・インターポーザは、特に最近Intelがガラス・ベースのテスト車両パッケージを発表した後、大きな関心を集めている。ガラスは、調整可能な熱膨張係数(CTE)、高い寸法安定性、滑らかで平坦な表面、パネル製造が可能といった有利な特性を備えており、シリコンに匹敵する配線機能を備えたインターポーザの有望な候補となっている。しかし、ガラス・インターポーザーの主な欠点は、技術的な課題に加えて、エコシステムが未成熟であることと、大規模な生産能力がないことである。エコシステムが成熟し、生産能力が向上すれば、半導体パッケージングにおけるガラスベースの技術はさらに成長し、採用されるかもしれない。
3Dパッケージング技術に関しては、Cu-Cuバンプレスハイブリッドボンディングが有力なイノベーションとして浮上している。この高度な技術は、SiO2などの誘電体材料と埋め込み金属(Cu)を組み合わせることにより、永久的な相互接続を実現します。Cu-Cuハイブリッド・ボンディングは、10マイクロメートル以下、典型的には1桁マイクロメートルのピッチを達成することができ、バンプ・ピッチが約40-50マイクロメートルである従来のマイクロバンプ技術に比べて大幅に改善されている。ハイブリッドボンディングの利点には、I/Oの増加、高帯域幅、3D垂直スタッキングの改善、電力効率の向上、アンダーフィルがないことによる寄生素子と熱抵抗の低減などがある。しかし、この技術は製造が複雑で、コストが高くなる。
半導体パッケージにおける相互接続技術の概要。出典 先進半導体パッケージング2025-2035
2.5Dおよび3Dパッケージング技術には、さまざまなパッケージング技術が含まれる。2.5Dパッケージングでは、インターポーザー材料の選択により、上図に示すように、Siベース、有機ベース、ガラスベースのインターポーザーに分類される。一方、3Dパッケージングでは、マイクロバンプ技術の進化により、より小さなピッチ寸法を目指している。しかし、現在では、Cu-Cuを直接接合するハイブリッド接合技術の採用により、1桁台のピッチ寸法を実現することが可能となり、この分野での大きな進歩を示している。
注目すべき2.5Dおよび3Dパッケージ開発の主な動向:
IDTechExは以前、2.5Dシリコンブリッジソリューションがシリコンインターポーザに代わってHPCチップのパッケージングの主要選択肢となる日が近いと予測した。NVIDIAや、GoogleやAmazonのような大手HPC開発企業に2.5Dシリコンインターポーザーを提供しているTSMCは最近、3.5倍レチクルサイズの第一世代CoWoS_Lの量産を発表した。IDTechExでは、この傾向は今後も続くと見ており、主要プレイヤーを網羅したレポートでさらなる進化を探っている。
Semicon Taiwan 2024で強調されたように、パネルレベルパッケージングが重要な焦点となっている。このパッケージング方式は、インターポーザーの大型化を可能にし、より多くのパッケージを同時に生産することでコスト削減に貢献する。その可能性にもかかわらず、反り管理などの課題に対処する必要がある。インターポーザーの大型化とコスト効率の向上に対する需要の高まりを反映し、その重要性が高まっている。
ガラスは、シリコンに匹敵する微細配線が可能で、熱膨張係数(CTE)の調整や信頼性の向上といった利点もある有力な候補として浮上している。また、ガラスインターポーザはパネルレベルパッケージングにも対応しており、より管理しやすいコストで高密度の配線ができる可能性があり、将来のパッケージング技術にとって有望なソリューションとなっています。
3D 銅-銅(Cu-Cu)ハイブリッドボンディングは、チップ間の超ファインピッチ垂直相互接続を可能にする重要な技術です。この技術は、SRAMとCPUをスタックするAMDのEPYCや、I/Oタイル上にCPU/GPUタイルをスタックするMI300シリーズなど、すでにいくつかのハイエンドサーバー製品で採用されている。ハイブリッドボンディングは、将来のHBMの進歩、特に16-Hiまたは20-Hiレイヤーを超えるDRAMスタックにおいて、極めて重要な役割を果たすと期待されている。
光インターコネクト技術は、電力効率の向上とともに、より高いデータスループットへのニーズの高まりにより、大きな牽引力となっています。コ・パッケージド・オプティクス(CPO)は、I/O帯域幅を向上させ、エネルギー消費量を削減するための重要なソリューションとして浮上しています。光通信は、従来の電気伝送に比べて、距離による信号劣化の低減、クロストークに対する感受性の低減、大幅な広帯域化など、複数の利点を備えている。これらの利点により、CPOはデータ集約的で電力効率の高いHPCシステムに理想的に適合します。
注目すべき主要市場
2.5Dおよび3Dパッケージング技術の開発を牽引する主要市場は、間違いなくハイパフォーマンス・コンピューティング(HPC)分野である。これらの高度なパッケージング手法は、ムーアの法則の限界を克服する上で極めて重要であり、単一パッケージ内でより多くのトランジスタ、メモリ、相互接続を可能にする。また、チップを分割することで、I/Oタイルを処理タイルから分離するなど、異なる機能ブロックにわたって最適なプロセス・ノード利用が可能になり、効率がさらに高まります。
HPC以外にも、先端パッケージング技術の採用によって成長する市場はある。5Gおよび6G分野では、アンテナ・イン・パッケージや最先端チップ・ソリューションのようなイノベーションが、将来の無線アクセス・ネットワーク(RAN)アーキテクチャを形成するでしょう。これらの技術は、安全性、信頼性、小型化、電力・熱管理、費用対効果を確保しながら、大量のデータを処理するセンサースイートとコンピューティングユニットの統合をサポートするため、自律走行車も恩恵を受けるでしょう。
スマートフォン、スマートウォッチ、AR/VR デバイス、PC、ワークステーションを含むコンシューマーエレクトロニクスは、コスト意識が高いものの、より小さなスペースでより多くのデータを処理することにますます重点を置くようになっている。先進的な半導体パッケージングはこのトレンドにおいて重要な役割を果たすが、そのパッケージング方法はHPCで使用されるものとは異なるだろう。IDTechExはこれらの産業について詳細な分析を行い、先端パッケージング技術がどのような影響を与えるかを検証し、市場予測を提供している。
先端半導体パッケージングの主要市場 出典 先端半導体パッケージング2025-2035
本レポートの内容
レポート「アドバンスト半導体パッケージング 2025-2035」は、半導体パッケージング技術の最新のイノベーションを徹底的に調査し、主要な技術動向を網羅し、バリューチェーンを分析し、主要プレイヤーを評価し、詳細な市場予測を提供しています。
次世代ICの基盤としての先端半導体パッケージングの重要な役割を認識し、AIやデータセンター、5G、自律走行車、民生用電子機器などの主要市場におけるアプリケーションに焦点を当てている。これらの分野におけるIDTechExの専門知識を活用することで、本レポートはこれらの重要分野におけるアドバンスト半導体パッケージングの影響と将来の軌道について包括的な理解を提供する。
本レポートの主な内容
先端半導体パッケージングの技術動向とメーカーを探る:
10年間のきめ細かな市場予測と分析:
Summary
Report Summary
The evolution of semiconductor packaging technologies
Semiconductor packaging has evolved from traditional 1D PCB designs to cutting-edge 3D hybrid bonding at the wafer level. This advancement allows for interconnect pitches in the single-digit micrometer range and bandwidths up to 1000 GB/s, all while maintaining high energy efficiency. Central to advanced semiconductor packaging technologies are 2.5D packaging—where components are positioned side by side on an interposer—and 3D packaging, which involves stacking active dies vertically. These technologies are critical for the future of HPC systems.
2.5D packaging technologies involve various interposer materials, each offering distinct advantages and drawbacks. Silicon (Si) interposers, which include full passive Si wafers and localized Si bridges, are known for facilitating the finest routing features, making them ideal for high-performance computing. However, they come with high costs in both materials and manufacturing, and face limitations in packaging area. To mitigate these issues, the use of localized Si bridges is increasing, strategically utilizing silicon where fine features are essential and addressing area constraints.
Organic interposers, which use a fan-out molding compound, offer a more cost-effective alternative to silicon. They have a lower dielectric constant, which reduces RC delay in the package. Despite these benefits, organic interposers struggle to achieve the same level of interconnect feature reduction as silicon-based packages, limiting their adoption in high-performance computing applications.
Glass interposers have gained significant interest, particularly after Intel's recent unveiling of a glass-based test vehicle package. Glass offers advantageous properties such as a tunable Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE), high dimensional stability, a smooth as well as flat surface, and the ability to enable panel manufacturing, making it a promising candidate for interposers with routing features that could rival silicon. However, the main drawback of glass interposers is the immature ecosystem and the current lack of large-scale production capabilities, in addition to its technical challenges. As the ecosystem matures and production capabilities improve, glass-based technologies in semiconductor packaging may see further growth and adoption.
Regarding 3D packaging technologies, Cu-Cu bumpless hybrid bonding is emerging as a leading innovation. This advanced technique creates permanent interconnections by combining a dielectric material, such as SiO2, with embedded metal (Cu). Cu-Cu hybrid bonding can achieve pitches below 10 micrometers, typically in the single-digit micrometer range, which is a significant improvement over conventional microbump technology, which has a bump pitch of around 40-50 micrometers. The benefits of hybrid bonding include increased I/O, higher bandwidth, improved 3D vertical stacking, enhanced power efficiency, and reduced parasitics and thermal resistance due to the absence of underfill. However, this technique is complex to manufacture and comes with higher costs.
Overview of interconnection technique in semiconductor packaging. Source: Advanced Semiconductor Packaging 2025-2035
The 2.5D and 3D packaging technologies encompass various packaging techniques. In 2.5D packaging, the choice of interposer material categorizes it into Si-based, Organic-based, and glass-based interposers, as illustrated in the figure above. Meanwhile, in 3D packaging, the evolution of microbump technology aims for smaller pitch dimensions. However, achieving single-digit pitch dimensions today is made possible through the adoption of hybrid bonding technology, a method that directly connects Cu-Cu, indicating a significant advancement in the field.
Key trends in 2.5D and 3D packaging development to watch:
IDTechEx has previously predicted that 2.5D silicon bridge solutions will soon replace silicon interposers as the primary choice for packaging HPC chips, due to the limitations of silicon interposers, which struggles to exceed 3x reticle sizes. TSMC, a key provider of 2.5D silicon interposers to NVIDIA and other major HPC developers like Google and Amazon, recently announced high-volume production of its first-generation CoWoS_L at 3.5x reticle size. IDTechEx expects this trend to continue, with further advancements explored in their report covering key players.
Panel-level packaging has become a significant focus, as highlighted at Semicon Taiwan 2024. This packaging method allows for larger interposers and helps reduce costs by enabling the production of more packages simultaneously. Despite its potential, challenges such as warpage management still need to be addressed. Its growing prominence reflects the increasing demand for larger and more cost-effective interposers.
Glass is emerging as a strong candidate for enabling fine routing, comparable to silicon, with added benefits like tunable coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) and improved reliability. Glass interposers are also compatible with panel-level packaging, offering the potential for high-density routing at a more manageable cost, making them a promising solution for future packaging technologies.
3D copper-copper (Cu-Cu) hybrid bonding is a critical technology for enabling ultra-fine pitch vertical interconnects between chips. This technology has already been used in several high-end server products, including AMD's EPYC for stacking SRAM and CPUs, and the MI300 series for stacking CPU/GPU tiles on I/O tiles. Hybrid bonding is expected to play a pivotal role in future HBM advancements, particularly for DRAM stacks beyond 16-Hi or 20-Hi layers.
Optical interconnect technology has gained considerable traction, driven by the growing need for higher data throughput alongside improved power efficiency. Co-packaged optics (CPO) is emerging as a key solution to enhance I/O bandwidth and reduce energy consumption. Optical communication offers multiple advantages over traditional electrical transmission, including lower signal degradation over distance, reduced susceptibility to crosstalk, and significantly higher bandwidth. These benefits make CPO an ideal fit for data-intensive, power-efficient HPC systems.
Key markets to watch
The primary market driving the development of 2.5D and 3D packaging technologies is undoubtedly the high-performance computing (HPC) sector. These advanced packaging methods are crucial in overcoming the limitations of Moore's law, enabling more transistors, memory, and interconnections within a single package. The disaggregation of chips also allows for optimal process node utilization across different functional blocks, such as separating I/O tiles from processing tiles, further enhancing efficiency.
Beyond HPC, other markets are poised for growth through the adoption of advanced packaging technologies. In the 5G and 6G sectors, innovations like antenna-in-package and cutting-edge chip solutions will shape the future of radio access network (RAN) architectures. Autonomous vehicles will also benefit, as these technologies support the integration of sensor suites and computing units to process large volumes of data while ensuring safety, reliability, compactness, power and thermal management, and cost-effectiveness.
Consumer electronics—including smartphones, smartwatches, AR/VR devices, PCs, and workstations—though more cost-conscious, are increasingly focused on handling more data within smaller spaces. Advanced semiconductor packaging will play a key role in this trend, though the packaging methods will differ from those used in HPC. IDTechEx provides in-depth analysis of these industries, examining how advanced packaging technologies will impact them and offering market forecasts.
Key markets for advanced semiconductor packaging. Source: Advanced Semiconductor Packaging 2025-2035
What is in this report?
The report "Advanced Semiconductor Packaging 2025-2035" thoroughly explores the latest innovations in semiconductor packaging technology, covering key technical trends, analyzing the value chain, evaluating major players, and providing detailed market forecasts.
Recognizing the crucial role of advanced semiconductor packaging as the foundation for next-generation ICs, the report focuses on its applications in key markets such as AI and data centers, 5G, autonomous vehicles, and consumer electronics. Leveraging IDTechEx's expertise in these sectors, the report delivers a comprehensive understanding of the impact and future trajectory of advanced semiconductor packaging in these critical fields.
Key aspects in this report:
Exploring Technology Trends and Manufacturers in Advanced Semiconductor Packaging:
10-year Granular Market Forecasts & Analysis:
Table of Contents
ご注文は、お電話またはWEBから承ります。お見積もりの作成もお気軽にご相談ください。本レポートと同分野(半導体)の最新刊レポート
IDTechEx社の 半導体、コンピュータ、AI - Semiconductors, Computing & AI分野 での最新刊レポート
よくあるご質問IDTechEx社はどのような調査会社ですか?IDTechExはセンサ技術や3D印刷、電気自動車などの先端技術・材料市場を対象に広範かつ詳細な調査を行っています。データリソースはIDTechExの調査レポートおよび委託調査(個別調査)を取り扱う日... もっと見る 調査レポートの納品までの日数はどの程度ですか?在庫のあるものは速納となりますが、平均的には 3-4日と見て下さい。
注文の手続きはどのようになっていますか?1)お客様からの御問い合わせをいただきます。
お支払方法の方法はどのようになっていますか?納品と同時にデータリソース社よりお客様へ請求書(必要に応じて納品書も)を発送いたします。
データリソース社はどのような会社ですか?当社は、世界各国の主要調査会社・レポート出版社と提携し、世界各国の市場調査レポートや技術動向レポートなどを日本国内の企業・公官庁及び教育研究機関に提供しております。
|
|




.png)
.png)

.png)
