ハイテク産業における希土類元素:中国の禁輸措置下での市場分析と予測Rare Earths Elements in High-Tech Industries: Market Analysis and Forecasts Amid Chinas Trade Embargo レアアースは、CMP研磨スラリーや半導体産業の高誘電率誘電体として使用されている。 STI平坦化スラリーで使用されるセリアの価格は、レアアース鉱山の97%を保有する中国による禁輸措置により、2009年か... もっと見る
サマリー
レアアースは、CMP研磨スラリーや半導体産業の高誘電率誘電体として使用されている。 STI平坦化スラリーで使用されるセリアの価格は、レアアース鉱山の97%を保有する中国による禁輸措置により、2009年から2010年にかけて1300%上昇した。本レポートでは、この禁輸措置が半導体、HDD、LCD、コンシューマー製品、グリーンテクノロジーなどのハイテク産業に与える影響を分析している。
レアアースはCMP研磨スラリーや半導体産業の高誘電率絶縁膜に使用されている。 STI平坦化スラリーで使用されるセリアの価格は、レアアース鉱山の97%を保有する中国による禁輸措置により、2009年から2010年にかけて1300%上昇した。本レポートでは、この禁輸措置が半導体、HDD、LCD、消費者製品、グリーンテクノロジーなどのハイテク産業に与える影響を分析している。
はじめに
当レポート「ハイテクおよび代替エネルギー産業におけるレアアース元素:本レポート「ハイテクおよび代替エネルギー産業におけるレアアース(希土類元素):市場分析と予測」は、ハイテクおよび代替エネルギー産業におけるレアアース(希土類元素)の重要な役割について包括的に調査したものです。
レアアース(希土類元素)は、化学的にユニークな17の元素からなるグループで、さまざまな最先端技術や再生可能エネルギーシステムに不可欠な構成要素です。電気自動車や風力タービンからスマートフォンや高度医療機器に至るまで、レアアースはさまざまな産業でイノベーションと持続可能性を実現する上で重要な役割を果たしています。
本レポートでは、レアアース市場の複雑なダイナミクスを掘り下げ、世界的なサプライチェーンの回復力、需要パターンの変化、価格決定力、地政学的影響などの要因を検証します。
詳細な洞察と予測を提供することで、本レポートは、サプライチェーンの混乱や地政学的緊張などの課題の中で、ハイテクおよび代替エネルギー産業の複雑な状況を乗り切るために必要な知識と戦略的洞察を関係者に提供することを目的としています。
ハイテクおよび代替エネルギー産業の動向
ハイテクおよび代替エネルギー産業におけるレアアース(希土類元素)の利用は広範囲にわたり、現代技術と再生可能エネルギーソリューションの進歩と効率に不可欠な幅広い用途をカバーしています。ここではその詳細について説明する:
エレクトロニクスと通信機器:レアアース(希土類元素)は、スマートフォン、コンピューター、薄型モニター、その他の電子機器の製造に欠かせない。ネオジム、プラセオジム、ジスプロシウムなどの元素は、スピーカー、ハードドライブ、小型モーターの磁石に使用されている。ユーロピウムとテルビウムは、蛍光体の役割を果たすことで、スクリーンの鮮やかな表示に貢献している。
先端光学とレーザー:ガドリニウム、エルビウム、イッテルビウムは、光ファイバーやレーザー技術に使用されている。これらの元素は、高速インターネット伝送や医療用レーザーの精度に不可欠である。
防衛および航空宇宙:サマリウムから作られるサマリウム・コバルト磁石は、精密誘導弾や衛星通信システムに利用されている。イットリウムやテルビウムのような希土類元素は、そのユニークな光学的・磁気的特性により、レーダーシステムやその他の防衛用電子機器に使用されている。
風力タービン:ネオジム、プラセオジム、ジスプロシウムは、風力タービンの発電機の強力な永久磁石に不可欠である。これらの磁石のおかげで、風速が低くても効率よく発電することができる。
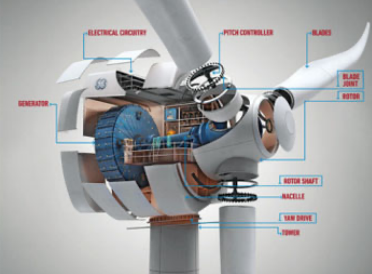
電気自動車(EV):電気自動車やハイブリッド車のトラクション・モーターには、ネオジム・鉄・ボロン(NdFeB)磁石が多く使用されています。この磁石の高性能は、EVの効率と航続距離に貢献している。
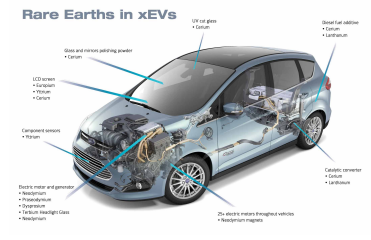
ソーラーパネル:希土類元素は太陽電池の主要成分ではないが、セリウムなどの希土類酸化物はソーラーパネルのガラス研磨に使用される。また、ランタンは、太陽エネルギーを貯蔵する高度な電池の製造に使用されている。
エネルギー貯蔵:ランタンやセリウムなどの希土類元素は、再生可能エネルギー貯蔵ソリューションに不可欠なニッケル水素電池に使用されている。これらの元素は電池の容量と寿命の向上に役立ち、再生可能エネルギー源の安定に不可欠である
傾向
ハイテク産業と代替エネルギー産業におけるレアアース(希土類元素)の動向は、さまざまな用途における重要な構成要素としての重要性の高まりを反映している。
顕著な傾向のひとつは、電気自動車(EV)や風力タービン、ソーラーパネルなどの再生可能エネルギー技術におけるレアアースの需要の高まりである。よりクリーンなエネルギー源への世界的な移行が加速するにつれて、NdPr永久磁石、触媒、電池技術に使用されるレアアースの需要は大幅に増加すると予想される。
さらに、特に地政学的緊張の観点から、サプライチェーンリスクを軽減し、一部の有力生産者への依存を減らすために、持続可能で多様なレアアース供給を確保することが重視されるようになっている。
さらに、材料科学と技術革新の進歩が、レアアースを抽出、精製し、さまざまな用途に利用するためのより効率的で環境に優しいプロセスの開発を後押ししている。
全体的な傾向として、ハイテクおよび代替エネルギー産業の発展におけるレアアースの重要な役割が強調される一方、持続可能で回復力のあるサプライチェーンを確保するための戦略的計画と協力の必要性が強調されている。
本レポートについて
ハイテクおよび代替エネルギー産業におけるレアアースレポートは、レアアースの生産、需要、市場ダイナミクス、技術進歩、将来展望に関する幅広いトピックをカバーしています。具体的には、以下の内容が含まれます:
市場分析:世界のレアアース市場の概要:過去の動向、現在の市場規模、成長予測、市場促進要因、課題、機会の詳細。
業界動向:電気自動車、再生可能エネルギー技術、民生用電子機器、先端製造業など、ハイテクおよび代替エネルギー分野におけるレアアース需要を形成する主要動向の調査。
サプライチェーン分析:主要生産者、採掘プロジェクト、加工施設、流通網を含むレアアース・サプライチェーンの調査。このセクションでは、地政学的要因、貿易政策、レアアースの入手可能性に影響を及ぼすサプライチェーンのリスクについても議論する。
用途の区分:磁石、電池、触媒、照明、電子機器、その他ハイテク製品での用途に焦点を当てた、様々な産業におけるレアアース用途の詳細分析。
技術革新:レアアース抽出、加工、リサイクル、代替の改善を目指した技術的進歩や研究イニシアチブの調査。このセクションでは、レアアースの効率と持続可能性を高めるための材料科学、製造プロセス、製品設計におけるイノベーションも取り上げる。
規制環境:レアアースの採掘、生産、取引、使用に影響を及ぼす規制の枠組み、環境規制、政策の概要。このセクションでは、持続可能性基準、責任ある調達イニシアティブ、レアアース関連産業のコンプライアンス要件も取り上げる。
市場予測:需要、供給、価格、市場シェアの予測を含む、レアアース市場の将来動向と成長機会の予測。このセクションは、レアアース分野の新技術、市場の混乱、投資の見通しに関する洞察を提供します。
競争状況:鉱業会社、加工業者、メーカー、エンドユーザーなど、レアアース業界の主要プレーヤーの分析。このセクションには、レアアースバリューチェーンにおける企業プロフィール、市場戦略、競争上の位置づけ、パートナーシップなどが含まれる。
全体として、この包括的なレポートは、ハイテクおよび代替エネルギー産業におけるレアアースの複雑な状況をナビゲートするために、実用的な洞察、戦略的提言、データに基づく分析を関係者に提供することを目的としています。
目次
目次
第1章 はじめに 1-1
1.1 レアアース元素の特徴 1-1
1.2 レアアース元素資源 1-4
1.3 レアアース元素応用の概要 1-10
第2章 レアアース産業 2-1
2.1 中国のレアアース産業 2-1
2.1.1 中国の生産量 2-3
2.1.2 中国のレアアース生産構造 2-7
2.1.3 中国のレアアース消費構造 2-12
2.1.4 中国のレアアース輸出 2-14
2.1.5 中国のレアアース産業の最近の活動 2-21
2.1.5.1 中国のレアアース産業の統合 2-21
2.1.5.2 輸出割当 2-23
2.2 世界のレアアース産業 2-24
2.2.1 米国 2-25
2.2.1.1 マウンテンパス 2-25
2.2.1.2 ユタ州レアアースプロジェクト 2-28
2.2.1.3 ベアロッジ・レアアース・プロジェクト 2-30
2.2.1.4 エルク・クリーク 2-32
2.2.1.5 ボカン・ドットソン・リッジ 2-34
2.2.1.6 ダイヤモンド・クリーク 2-36
2.2.1.7 レミ・パス 2-35
2.2.2 カナダ 2-40
2.2.2.1 マクラウド湖プロジェクト 2-40
2.2.2.2 ホイダス湖 2-40
2.2.2.3 ベンジャミン川プロジェクト 2-41
2.2.2.4 ダグラス川プロジェクト 2-43
2.2.2.5 ネカラチョ希土類元素プロジェクト 2-44
2.2.2.6 Archie Lake 2-47
2.2.2.7 Bulstrode 希土類鉱区 2-48
2.2.2.8 Mount Copeland 2-48
2.2.2.9 Cross Hills Newfoundland 2-50
2.2.2.10 Kipawa 2-51
2.2.2.11 Strange Lake 2-52
2.2.2.12 Ytterby 2-52
2.2.2.13 Grevet REE 2-54
2.2.2.14 Turner Falls 2-55
2.2.3 南アフリカ 2-56
2.2.3.1 Steenkampskraal Mine 南アフリカ 2-56
2.2.4 オーストラリア 2-57
2.2.4.1 Nolans Bore 2-57
2.2.4.2. マウント・ウェルド 2-60
2.2.4.3 ジャングル・ウェル/ラバートン 2-62
2.2.5 グリーンランド 2-63
2.2.5.1 クヴァネフイェルド・プロジェクト 2-63
2.2.6 アルゼンチン 2-65
2.2.6.1 クエバ・デル・チャチョ 2-65
2.2.6.2 Susques Property - Jujuy Province 2-67
2.2.6.3 John Galt Project 2-68
2.2.7 India 2-69
2.2.7.1 Indian Rare Earth 2-69
2.2.8 Russia 2-70
2.2.8.1 Kutessay II 2-70
2.3 鉱業企業のプロファイル 2-72
第3章 レアアース市場分析 3-1
3.1 概要 3-1
3.2 レアアース市場 3-4
3.2.1 国内生産と消費 3-4
3.2.2 中国生産と消費 3-12
3.3 世界のレアアース市場分析 3-19
第4章 ハイテク用途への影響 4-1
4.1 概要 4-1
4.1.1 用途別レアアース市場 4.1
4.1.2 NdPr磁石 4.4
4.2 半導体 4-12
4.2.1影響を受ける技術4-12
4.2.1.1 High-k 誘電体 4-12
4.2.1.2 研磨粉 4-15
4.2.2 使用されるレアアース 4-18
4.2.3 影響を受ける半導体デバイス/材料の市場予測 4-19
4.3 ハードディスクドライブ(HDD) 4-22
4.3.1 影響を受ける技術 4-22
4.3.1.1 HDD用ネオ磁石 4-23
4.3.1.2 高強度ガラス基板 4-25
4.3.1.3 研磨材料 4-25
4.3.2 使用されるレアアース 4-26
4.3.3 影響を受けるHDDデバイス/材料の市場予測 4-27
4.4 モバイル/モバイルインターネットデバイス 4-30
4.4.1 影響を受ける技術 4-30
4.4.2 使用されるレアアース 4-30
4.4.3 影響を受けるモバイルデバイス/材料の市場予測 4-31
4.5 Solid State Lighting ?LED/CFL 4-33
4.5.1 影響を受ける技術 4-33
4.5.1.1 発光ダイオード(LED)用蛍光体 4-33
4.5.1.2 小型蛍光ランプ(CFL)用蛍光体 4-35
4.5.2 使用されるレアアース 4-39
4.5.3 影響を受けるLEDデバイス/材料の市場予測 4-39
4.6 グリーンテクノロジー 4-42
4.6.1 影響を受ける技術 4-42
4.6.1.1 ハイブリッド車両用電気モーターおよびブレーキ用の磁石4-42
4.6.1.2 風力タービン用ネオ磁石 4-44
4.6.1.3 自動車用触媒コンバーター用セリウム 4-48
4.6.2 使用レアアース 4-50
4.6.3 影響を受けるグリーン・デバイス/材料の市場予測 4-53
4.6.4 その他のグリーン技術 4-57
第5章.米国戦略金属の視点 5-1
5.1 国防におけるレアアース金属の応用 5-1
5.2 戦略的課題:2024 年における米国の中国へのレアアース依存 5-2
5.2.1 中国のレアアースサプライチェーン管理 5-2
5.2.2 国家安全保障と防衛への懸念 5-3
5.3 2024 年における戦略的イニシアティブと取り組み 5-3
5.3.1 国内能力の構築 5-3
5.3.2 官民パートナーシップと資金調達イニシアティブ 5-4
5.3.3 海外依存の削減と同盟国の強化 5-5
5.4 サプライチェーンの問題 5-5
5.5 世界価格:中国のレアアース供給支配の影響 5-8
第6章 欧州の戦略的金属展望 6-1
6.1 重要性の評価 6-1
6.2 2020年EU重要原材料リスト 6-4
6.3 現在および過去の取り組み 6-7
6.4 レアアースサプライチェーンにおける欧州の革新と技術 6-12
6.4.1 レアアース代替における研究と革新 6-12
6.4.2 先進的レアアースリサイクル技術 6-13
6.4.3 資源探査におけるデジタル技術 6-13
6.4.4 欧州のレアアース戦略における官民パートナーシップ 6-14
第7章 米国のサプライチェーン再構築 7-1
7.1 材料サプライチェーンの課題と機会 7-1
7.1.1 米国におけるREO/RE処理 7-2
7.2.1 米国におけるレアアース(REE)/レアアース酸化物(REO)のリサイクル 7-7
7.2.1.1 全体プロセス 7-8
7.2.1.2 希土類磁石のリサイクル 7-9
7.2.1.3 希土類磁石の新たな代替品 7-12
7.2.1.4 蛍光体のリサイクル 7-14
図表リスト表
1.1 選択されたレアアース元素ベアリング製品 1-13
1.2 レアアース元素とその最終用途の一部 1-14
2.1 2015年以降のレアアース精鉱生産量 2-8
2.2 世界の鉱山生産量 2-11
2.3 世界のレアアース需給 2-13
2.4 中国のレアアース輸出量および輸出額 2-15
2.5 中国の元素別レアアース輸出 2-19
2.6 中国レアアース中国外プロジェクト 2-20
3.1 米国レアアース統計 3-5
3.2 レアアース価格 3-11
3.3 中国レアアース酸化物鉱山別予測 2019-2030 3-15
3.4 ROWレアアース酸化物鉱山別予測 2019-2030 3-16
3.5 レアアース供給-酸化物需要予測 3-20
3.6 最終用途別レアアース組成 3-28
4.1 NdFeB磁石用途別需要 4-7
4.2 NdFeB永久磁石需要の主要前提条件 4-9
4.3 NdPr酸化物の供給市場予測 4-10
4.4 NdPr酸化物の需要市場予測 4-11
4.5 半導体用セリアCMPスラリーの市場予測 4-20
4.6 ハードディスクドライブ用磁石の市場予測 4-28
4.7 HDDガラスディスク用セリアスラリーの市場予測 4-29
4.8 スマートフォン用レアアースの市場予測 4-32
4.9 LED用希土類蛍光体の市場展望 4-40
4.10 CFL用希土類蛍光体の市場展望 4-41
4.11 電気自動車用磁石の市場展望 4-54
4-12 内燃機関自動車用セリアの市場展望 4-55
4-13 風力タービン用磁石の市場展望 4-56
7.1 NdFeB永久磁石のサプライチェーンステップ7-4
図
1.1 レアアース元素の周期表 1-2
1.2 レアアース元素の存在量 1-5
1.3 1994年以降のレアアース生産量 1-9
1.4 中国のレアアース支配 1-12
2.1 中国におけるレアアースの割合と分布 2-4
2.2 1994年以降のレアアース酸化物の生産量 2-9
2.3 中国の企業別採掘割当量 2-16
2.4 中国のレアアース酸化物の輸出先別輸出量 2-17
2.5 中国のレアアース金属輸出先別 2-18
3.1 レアアース精製製品の米国分布 3-7
3.2 レアアース価格指数 3-10
3.3 中国と世界のレアアース生産の比較 3-18
3.4 世界のレアアース酸化物需給予測 3-21
3.5 レアアース需要量別 3-22
3.6 レアアース需要額別 3-23
3.7 レアアース用途量別 3-25
3.3-26
3.9 最終用途別レアアース組成 3-29
4.1 レアアース用途の数量シェア 4-3
4.2 用途別高性能磁石需要 4-6
4.3 用途別高性能磁石シェア-2030年 4-8
4.4 MOSFETとゲート酸化物の図解 4-13
4.5 セリアを用いたSTI CMP 4-17
4.6 ハイテク用途のハフニウム需要 4-21
4.7 HDDドライブとネオ磁石 4-24
4.8 蛍光灯のサプライチェーン 4-38
4.9 EVレアアース用途 4-43
4.10 風力タービンモーター 4-45
4.11 永久磁石のサプライチェーン 4-47
4.12 自動車用触媒コンバーター 4-49
5.1 NdPr磁石の需給関係 5-10
7.1 MP材料のプロセスフロー 7-3
7.2 磁気リサイクルプロセス 7-10
Summary
Rare earth elements are used in CMP polishing slurries and as high-k dielectrics in the semiconductor industry. Prices of ceria, used in STI planarization slurries increased 1300% between 2009 and 2010 because of an embargo by China, home to 97% of the rare earth mines. This report analyzes the impact of the embargo on high-tech industries such as semiconductors, HDDs, LCDs, consumer products, and green technology.
Rare earth elements are used in CMP polishing slurries and as high-k dielectrics in the semiconductor industry. Prices of ceria, used in STI planarization slurries increased 1300% between 2009 and 2010 because of an embargo by China, home to 97% of the rare earth mines. This report analyzes the impact of the embargo on high-tech industries such as semiconductors, HDDs, LCDs, consumer products, and green technology.
Introduction
The report "Rare Earths Elements in High-Tech and Alternative Energy Industries: Market Analysis and Forecasts" presents a comprehensive exploration into the pivotal role of rare earth elements (REEs) within high-tech and alternative energy sectors.
Rare earth elements, a group of 17 chemically unique elements, are integral components in a wide array of cutting-edge technologies and renewable energy systems. From electric vehicles and wind turbines to smartphones and advanced medical devices, REEs play a vital role in enabling innovation and sustainability across various industries.
This report delves into the intricate dynamics of the REEs market, examining factors such as global supply chain resilience, evolving demand patterns, pricing dynamics, and geopolitical influences.
By providing in-depth insights and forecasts, the report aims to empower stakeholders with the knowledge and strategic insights necessary to navigate the complex landscape of high-tech and alternative energy industries amid challenges such as supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions.
High-Tech and Alternative Energy Industries Trends
The utilization of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) in high-tech and alternative energy industries is extensive, covering a wide range of applications essential for the advancement and efficiency of modern technologies and renewable energy solutions. Here's a detailed exploration:
High-Tech Industries Discussed in Report
Electronics and Communication Devices: REEs are pivotal in manufacturing smartphones,computers, flat-screen monitors, and other electronic devices. Elements like neodymium,praseodymium, and dysprosium are used in magnets for speakers, hard drives, and small motors. Europium and terbium contribute to the vibrant displays of screens through their role in phosphors.
Advanced Optics and Lasers: Gadolinium, erbium, and ytterbium are used in optical fibers and laser technology. These elements are crucial for high-speed internet transmission and precision in medical lasers.
Defense and Aerospace: Samarium-cobalt magnets, made from samarium, are utilized in precision-guided munitions, and satellite communication systems. REEs like yttrium and terbium are used in radar systems and other defense electronics due to their unique optical and magnetic properties.
Alternative Energy Industries Discussed in Report
Wind Turbines: Neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium are essential for the powerful permanent magnets in the generators of wind turbines. These magnets allow the turbines to generate electricity efficiently, even at low wind speeds.

Electric Vehicles (EVs): The traction motors in electric and hybrid vehicles often use neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets. The high performance of these magnets contributes to the efficiency and range of EVs.

Solar Panels: While REEs are not major components in photovoltaic cells, certain rare earth oxides like cerium are used for polishing the glass of solar panels. Additionally, lanthanum is used in the production of advanced batteries that store solar energy.
Energy Storage: REEs like lanthanum and cerium are used in nickel-metal hydride (NiMH)batteries, which are crucial for renewable energy storage solutions. These elements help improve the battery's capacity and longevity, essential for the stability of renewable energy sources
Trends
The trends in Rare Earth Elements (REEs) within high-tech and alternative energy industries reflect their increasing importance as critical components in various applications.
One prominent trend is the growing demand for REEs in electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy technologies such as wind turbines and solar panels. As the global transition toward cleaner energy sources accelerates, the demand for REEs used in NdPr permanent magnets, catalysts, and battery technologies is expected to rise significantly.
Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on securing sustainable and diversified REE supplies to mitigate supply chain risks and reduce dependence on a few dominant producers, particularly in light of geopolitical tensions.
Another trend is the exploration of alternative sources and recycling methods to address supply constraints and environmental concerns associated with traditional REE mining and processing.Furthermore, advancements in material science and technological innovations are driving the development of more efficient and environmentally friendly processes for extracting, refining, and utilizing REEs in various applications.
Overall, the trends underscore the critical role of REEs in advancing high-tech and alternative energy industries while highlighting the need for strategic planning and collaboration to ensure a sustainable and resilient supply chain.
About This Report
Rare Earths Elements in High-Tech and Alternative Energy Industries report covers a wide range of topics related to the production, demand, market dynamics, technological advancements, and future prospects of REEs. Specifically, the report include:
Market Analysis: An overview of the global REE market, including historical trends, current market size, and growth projections, detailing market drivers, challenges, and opportunities.
Industry Trends: Exploration of key trends shaping the demand for REEs in high-tech and alternative energy sectors, such as electric vehicles, renewable energy technologies, consumer electronics, and advanced manufacturing.
Supply Chain Analysis: Examination of the REE supply chain, including major producers, mining projects, processing facilities, and distribution networks. This section also discusses geopolitical factors, trade policies, and supply chain risks affecting REE availability.
Application Segmentation: Detailed analysis of REE applications across various industries, highlighting their uses in magnets, batteries, catalysts, lighting, electronics, and other high-tech products.
Technology Innovation: Exploration of technological advancements and research initiatives aimed at improving REE extraction, processing, recycling, and substitution. This section also covers innovations in material science, manufacturing processes, and product design to enhance REE efficiency and sustainability.
Regulatory Environment: Overview of regulatory frameworks, environmental regulations, and policies impacting REE mining, production, trade, and usage. This section also addresses sustainability standards, responsible sourcing initiatives, and compliance requirements for REErelated industries.
Market Forecasts: Forecasting of future trends and growth opportunities in the REE market, including projections for demand, supply, prices, and market shares. This section provides insights into emerging technologies, market disruptions, and investment prospects in the REE sector.
Competitive Landscape: Analysis of key players in the REE industry, including mining companies, processors, manufacturers, and end-users. This section includes company profiles, market strategies, competitive positioning, and partnerships in the REE value chain.
Overall, the comprehensive report aims to provide stakeholders with actionable insights, strategic recommendations, and data-driven analyses to navigate the complex landscape of REEs in high-tech and alternative energy industries.
Table of Contents
Table Of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction 1-1
1.1 Rare Earth Element Characteristics 1-1
1.2 Rare Earth Element Resources 1-4
1.3 Overview of Rare Earth Element Applications 1-10
Chapter 2 Rare Earth Industry 2-1
2.1 China’ Rare Earth Industry 2-1
2.1.1 China’s Production 2-3
2.1.2 China Rare Earth Production Structure 2-7
2.1.3 China Rare Earth Consumption Structure 2-12
2.1.4 China Export of Rare Earths 2-14
2.1.5 Recent Activities Of China’s Rare Earth Industry 2-21
2.1.5.1 Consolidation Of China’s Rare Earth Industry 2-21
2.1.5.2 Export Quotas 2-23
2.2 Rest Of World’s Rare Earth Industry 2-24
2.2.1 United States 2-25
2.2.1.1 Mountain Pass 2-25
2.2.1.2 Utah Rare Earth Project 2-28
2.2.1.3 Bear Lodge Rare-Earth Project 2-30
2.2.1.4 Elk Creek 2-32
2.2.1.5 Bokan-Dotson Ridge 2-34
2.2.1.6 Diamond Creek 2-36
2.2.1.7 Lemhi Pass 2-35
2.2.2 Canada 2-40
2.2.2.1 MacLeod Lake Project 2-40
2.2.2.2 Hoidas Lake 2-40
2.2.2.3 Benjamin River Project 2-41
2.2.2.4 Douglas River Project 2-43
2.2.2.5 Nechalacho Rare Earth Element Project 2-44
2.2.2.6 Archie Lake 2-47
2.2.2.7 Bulstrode Rare Earth Property 2-48
2.2.2.8 Mount Copeland 2-48
2.2.2.9 Cross Hills Newfoundland 2-50
2.2.2.10 Kipawa 2-51
2.2.2.11 Strange Lake 2-52
2.2.2.12 Ytterby 2-52
2.2.2.13 Grevet REE 2-54
2.2.2.14 Turner Falls 2-55
2.2.3 South Africa 2-56
2.2.3.1 Steenkampskraal Mine South Africa 2-56
2.2.4 Australia 2-57
2.2.4.1 Nolans Bore 2-57
2.2.4.2 Mount Weld 2-60
2.2.4.3 Jungle Well/ Laverton 2-62
2.2.5 Greenland 2-63
2.2.5.1 Kvanefjeld Project 2-63
2.2.6 Argentina 2-65
2.2.6.1 Cueva del Chacho 2-65
2.2.6.2 Susques Property - Jujuy Province 2-67
2.2.6.3 John Galt Project 2-68
2.2.7 India 2-69
2.2.7.1 Indian Rare Earth 2-69
2.2.8 Russia 2-70
2.2.8.1 Kutessay II 2-70
2.3 Profiles of Mining Corporations 2-72
Chapter 3 Rare Earth Market Analysis 3-1
3.1 Overview 3-1
3.2 Rare Earth Market 3-4
3.2.1 Domestic Production and Consumption 3-4
3.2.2 China Production and Consumption 3-12
3.3 Global Rare Earth Market Analysis 3-19
Chapter 4 Impact on Hi-Tech Applications 4-1
4.1 Overview 4-1
4.1.1 Rare Earth Market By Application 4.1
4.1.2 NdPr Magnets 4.4
4.2 Semiconductors 4-12
4.2.1 Technology Impacted 4-12
4.2.1.1 High-k Dielectrics 4-12
4.2.1.2 Polishing Powders 4-15
4.2.2 Rare Earth Material Used 4-18
4.2.3 Market Forecast of Impacted Semiconductor Devices/Materials 4-19
4.3 Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) 4-22
4.3.1 Technology Impacted 4-22
4.3.1.1 Neo Magnets for HDDs 4-23
4.3.1.2 High Strength Glass Substrates 4-25
4.3.1.3 Polishing Materials 4-25
4.3.2 Rare Earth Material Used 4-26
4.3.3 Market Forecast of Impacted HDD Devices/Materials 4-27
4.4 Mobile and Mobile Internet Devices 4-30
4.4.1 Technology Impacted 4-30
4.4.2 Rare Earth Material Used 4-30
4.4.3 Market Forecast of Impacted Mobile Devices/Materials 4-31
4.5 Solid State Lighting – LED/CFL 4-33
4.5.1 Technology Impacted 4-33
4.5.1.1 Phosphors for Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) 4-33
4.5.1.2 Phosphors for Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFL) 4-35
4.5.2 Rare Earth Material Used 4-39
4.5.3 Market Forecast of Impacted LED Devices/Materials 4-39
4.6 Green Technology 4-42
4.6.1 Technology Impacted 4-42
4.6.1.1 Magnets for Hybrid Vehicle Electric Motors and Brakes 4-42
4.6.1.2 Neo Magnets for Wind Turbines 4-44
4.6.1.3 Cerium for Catalytic Converters for Automobiles 4-48
4.6.2 Rare Earth Material Used 4-50
4.6.3 Market Forecast of Impacted Green Devices/Materials 4-53
4.6.4 Other Green Technologies 4-57
Chapter 5. U.S Strategic Metal Perspective 5-1
5.1 The Application of Rare Earth Metals in National Defense 5-1
5.2 Strategic Issues: U.S. Dependency On China For Rees In 2024 5-2
5.2.1 China's Control Of The Rare Earth Supply Chain 5-2
5.2.2 National Security And Defense Concerns 5-3
5.3 Strategic Initiatives And Efforts In 2024 5-3
5.3.1 Building Domestic Capacity 5-3
5.3.2 Public-Private Partnerships And Funding Initiatives 5-4
5.3.3 Reducing Foreign Dependency And Strengthening Allies 5-5
5.4 Supply Chain Issues 5-5
5.5 Global Price: Impact Of China's Rare Earth Supply Dominance 5-8
Chapter 6 European Strategic Metal Perspective 6-1
6.1 Assessing Criticality 6-1
6.2 The 2020 EU Critical Raw Materials List 6-4
6.3 Current And Past Initiatives 6-7
6.4 European Innovation and Technology in RE Supply Chains 6-12
6.4.1 Research and Innovation in RE Substitution 6-12
6.4.2 Advanced Rare Earth Recycling Technologies 6-13
6.4.3 Digital Technologies in Resource Exploration 6-13
6.4.4 Public-Private Partnerships in Europe’s Rare Earth Strategy 6-14
Chapter 7 Rebuilding a U.S. Supply Chain 7-1
7.1 Materials Supply Chain Challenges And Opportunities 7-1
7.1.1 REO/REE Processing In U.S. 7-2
7.2 Supply Chain Resiliency And China’s Dominance 7.6
7.2.1 REE/REO Recycling in U.S. 7-7
7.2.1.1 Overall Process 7-8
7.2.1.2 Recycling RE Magnets 7-9
7.2.1.3 Emerging Alternatives To Rare Earth Magnets 7-12
7.2.1.4 Recycling Phosphors 7-14
List of Tables/GraphsTABLES
1.1 Selected Rare Earth Element Bearing Products 1-13
1.2 Rare Earths Elements And Some Of Their End Uses 1-14
2.1 Production Of Rare Earth Concentrates Since 2015 2-8
2.2 World Mine Production 2-11
2.3 Global Rare Earth Supply/Demand 2-13
2.4 China's Rare Earth Export Volume And Export Amount 2-15
2.5 China's Rare Earth Exports By Element 2-19
2.6 China Rare Earth Projects Outside China 2-20
3.1 U.S. Rare Earth Statistics 3-5
3.2 Rare Earth Prices 3-11
3.3 China Rare Earths Oxide Forecast By Mine 2019-2030 3-15
3.4 ROW Rare Earths Oxide Forecast By Mine 2019-2030 3-16
3.5 Rare Earth Supply-Oxide Demand Forecast 3-20
3.6 Rare Earth Composition By End Use 3-28
4.1 NdFeB Magnet Demand By Application 4-7
4.2 NdFeB Permanent Magnet Market Demand Key Assumptions 4-9
4.3 NdPr Oxide Supply Market Forecast 4-10
4.4 NdPr Oxide Demand Market Forecast 4-11
4.5 Market Forecast of Ceria CMP Slurry for Semiconductors 4-20
4.6 Market Forecast of Magnets for Hard Disk Drives 4-28
4.7 Market Forecast of Ceria Slurry For HDD Glass Disks 4-29
4.8 Market Forecast of Rare Earths for Smartphones 4-32
4.9 Market Forecast of Rare Earth Phosphors for LEDs 4-40
4.10 Market Forecast of Rare Earth Phosphors for CFLs 4-41
4.11 Market Forecast Of Magnets For Electric Vehicles 4-54
4-12 Market Forecast Of Ceria For Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles 4-55
4-13 Market Forecast Of Magnets For Wind Turbines 4-56
7.1 NdFeB Permanent Magnet Supply Chain Steps 7-4
FIGURES
1.1 Periodic Table Of Rare Earth Elements 1-2
1.2 Abundance Of The Rare Earth Elements 1-5
1.3 Rare Earth Production Since 1994 1-9
1.4 China’s Rare Earth Dominance 1-12
2.1 Rare Earth Proportion And Distribution In China 2-4
2.2 Production Of Rare Earth Oxides Since 1994 2-9
2.3 China Mining Quota By Company 2-16
2.4 China Rare Earth Oxide Exports By Destination 2-17
2.5 China Rare Earth Metal Exports By Destination 2-18
3.1 U.S. Distribution Of Refined Rare Earth Products 3-7
3.2 Rare-Earth Price Index 3-10
3.3 Comparison Of Rare Earth Production in China And The World 3-18
3.4 Global Rare Earth Oxide Supply-Demand Forecast 3-21
3.5 REE Demand By Volume 3-22
3.6 REE Demand By Value 3-23
3.7 REE Applications By Volume 3-25
3.8 REE Applications By Value 3-26
3.9 REE Composition By End Use 3-29
4.1 Rare Earth Application Market Share by Volume 4-3
4.2 High-Performance Magnet Demand by Application 4-6
4.3 High-Performance Magnet Share by Application - 2030 4-8
4.4 Illustration of MOSFET and Gate Oxide 4-13
4.5 STI CMP Using Ceria 4-17
4.6 Hafnium Demand for High-Tech Applications 4-21
4.7 HDD Drive and Neo Magnets 4-24
4.8 Supply Chain for Fluorescent Lighting 4-38
4.9 EV Rare Earths Applications 4-43
4.10 Wind Turbine Motor 4-45
4.11 Supply Chain for Permanent Magnets 4-47
4.12 Catalytic Converter for Automobiles 4-49
5.1 NdPr Magnet Supply-Demand 5-10
7.1 MP Materials Process Flow 7-3
7.2 Magnetic Recycling Process 7-10
ご注文は、お電話またはWEBから承ります。お見積もりの作成もお気軽にご相談ください。本レポートと同分野(金属材料)の最新刊レポート
The Information Network社の 半導体プロセスレポートシリーズ分野 での最新刊レポートよくあるご質問The Information Network社はどのような調査会社ですか?インフォメーションネットワーク (The Information Network) は、半導体製造に関連する材料や半導体のエンドアプリケーションなどの市場を幅広く調査・分析する米国ペンシルベニア州の調... もっと見る 調査レポートの納品までの日数はどの程度ですか?在庫のあるものは速納となりますが、平均的には 3-4日と見て下さい。
注文の手続きはどのようになっていますか?1)お客様からの御問い合わせをいただきます。
お支払方法の方法はどのようになっていますか?納品と同時にデータリソース社よりお客様へ請求書(必要に応じて納品書も)を発送いたします。
データリソース社はどのような会社ですか?当社は、世界各国の主要調査会社・レポート出版社と提携し、世界各国の市場調査レポートや技術動向レポートなどを日本国内の企業・公官庁及び教育研究機関に提供しております。
|
|






