中性原子方式の量子コンピューター市場Markets for Neutral Atom Quantum Computers IQTリサーチは、中性原子量子コンピュータが、支配的な超伝導量子コンピュータのパラダイムへの挑戦であると同時に、さらに高度なマシンへの道筋を示す「主力」量子コンピュータとして台頭してくると考えてい... もっと見る

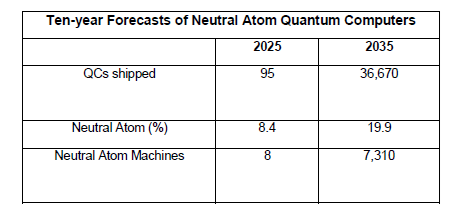
サマリーIQTリサーチは、中性原子量子コンピュータが、支配的な超伝導量子コンピュータのパラダイムへの挑戦であると同時に、さらに高度なマシンへの道筋を示す「主力」量子コンピュータとして台頭してくると考えている。IQT Researchは、2025年にはわずか8台のニュートラル・アトム・マシンが出荷されるが、この数は2035年までに7310台以上のニュートラル・アトム・マシンに成長すると考えている。 本レポート「中性原子量子コンピュータの市場」は、世界の主要な中性原子量子コンピュータベンダーの製品/市場戦略を分析している。Atom Computing、Atom Quantum Labs、Infleqtion、M Squared、OpenQuantum、Pasqal、PlanQC、QuERAなどである。また、チップメーカーや部品メーカーが中性原子マシンに見出しているビジネスチャンスについても掘り下げている。チップ/コンポーネント分野で著名な企業には、AMD、浜松ホトニクス、NanoQT、Nu Quantum、QBlox、Topticaなどがある。 本レポートでは、中性原子量子コンピュータの成功に拍車をかけている主要な技術動向についても分析している。これには、サイズ、重量、消費電力を改善するためのフォトニック集積回路(PIC)の使用、中性原子マシンを最適にサポートする新しい材料プラットフォーム、中性原子マシンの大規模な政府機関や研究施設での使用からHPCやデータセンターへの移行などが含まれる。中性原子量子コンピュータにとって本当に重要なことは、$/Qubitが魅力的であり続けることである。IQT Researchは、中性原子技術は量子業界紙でますます肯定的に描かれていると指摘している。今のところ、Amazon BraketとAzure Quantumが、中性原子量子コンピュータにアクセスする唯一の一般的な方法である。 目次 報告書 IQT-NAQC2025-0525 公開:2025 年 5 月 20 日 目次 中性原子 第1章 中性原子の技術と製品 1.1 技術の進化 1.1.1 使用される原子 1.1.2 ポジティブに捉えられつつある中性原子 1.1.3 アクセスのしやすさ 1.2 中性原子コンポーネント 1.2.1 原子制御ハードウェアと読み出しコンポーネント 1.2.2 フォトニックおよびフォトグラフィック・コンポーネント 1.2.3 クライオスタット 1.3 中性原子関連ソフトウェア 1.3.1 研究所での作業 第2章 市場と起源 2.1 目標とする用途と可能性 2.1.1 ニュートラルアトムコンピュータ上の分散量子コンピューティング 2.1.2 データセンターにおける中性原子コンピュータ 2.1.3 ニュートラル・アトムコンピューターのその他の用途 2.2 制御とエコシステム 2.3 中性原子コンピューターの供給構造 2.4 ナショナルな問題 2.4.1 ニュートラル・アトムコンピュータの世界市場と国内市場 2.4.2 関税の問題 第3章ニュートラル・アトム技術 3.1 ニュートラル・アトム・コンピューティング 3.1.1 アトムコンピューティング(アメリカ) 3.1.2 Atom Quantum Labs(スロベニア) 3.1.3 Infleqtion(米国) 3.1.4 Mスクエアード(イギリス) 3.1.5 OpenQuantum(イギリス) 3.1.6 Pasqal(フランス) 3.1.7 PlanQC(ドイツ) 3.1.8 QuEra Computing(米国) 3.2 ニュートラルAtomコンポーネントとサブシステム 3.2.1 AMD(米国) 3.2.2 浜松ホトニクス(日本) 3.2.3 レイクショア・クライオトロニクス(米国) 3.2.4 メンロシステムズ(ドイツ) 3.2.5 ナノQT(日本) 3.2.6 ネクサスフォトニクス(米国) 3.2.7 Nu Quantum(イギリス) 3.2.8 OpenQuantum(グローバル) 3.2.9 Qblox(オランダ) 3.2.10 Quantum Machines(イスラエル) 3.2.11 サンディア国立研究所(アメリカ) 3.2.12 トプティカ・フォトニクス(ドイツ) 3.2.13 Vescent(アメリカ) 3.3 ソフトウェア 3.3.1 Agnostiq(カナダ) 3.3.2 DarkStarStrix(ユーザー名)(米国) 3.3.3 data cybernetics ssc GmbH(ドイツ) 3.3.4 ローレンス・バークレー国立研究所(LBNL)(米国) 3.3.5 M-Labs(香港) 3.3.6 マイクロソフト(米国) 3.3.7 Q-CTRL(オーストラリア) 3.3.8 QMWare(スイス) 3.3.9 QPerfect(フランス) 3.3.10 SimuQ(アメリカ) 3.3.11 ウルフラム(米国) 3.4 プラットフォーム 3.4.1 Amazon Braket(米国) 3.4.2 qBraid(米国) 3.4.3 ストラングワークス(米国) 3.5 国内および国際センター 3.5.1 科学技術省(DOST)(フィリピン) 3.5.2 欧州量子科学センター(CESQ)(フランス) 3.5.3 科学技術振興機構(日本) 3.5.4 国立量子コンピューティングセンター(NQCC)(イギリス) 3.5.5 ロシア量子センター(ロシア) 第4章:中性原子コンピュータの10年予測 4.1 予測の考え方 4.2 予測とその使い方と不確実性 アナリストについて 図表 図表4-1:中性原子量子コンピューターの10年予測
プレスリリース中性原子方式の量子コンピューターは2035年までに出荷台数を7,300台以上に拡大量子技術に特化したレポートを発行するInside Quantum Technology (インサイドクァンタムテクノロジー)リサーチは、最新レポート「中性原子方式の量子コンピューター市場」において、中性原子量子コンピューターは2035年までに出荷台数を7,300台以上に拡大すると見込んでいる。
2025年5月28日|プレスリリース
中性原子量子コンピューターにとって本当に重要なのは、$/Qubitが魅力的であり続けることである。
中性原子方式量子コンピューター出荷予測:2025年-2035年
SummaryIQT Research believes Neutral Atom Quantum Computers are emerging as "workhorse" quantum computers that are both a challenge to the dominant superconducting quantum computing paradigm and a path forward to even more advanced machines. IQT Research believes that in 2025, only eight neutral atom machines will be shipped but this number will grow to more than 7,310 neutral atom machines by 2035. This report, “Markets for Neutral Atom Quantum Computers” analyzes the product/market strategies of the leading neutral atom quantum computer vendors worldwide. These include Atom Computing, Atom Quantum Labs, Infleqtion, M Squared, OpenQuantum, Pasqal, PlanQC, and QuERA. But we also dig into the opportunities that the chip and component makers have been finding in neutral atom machines. Prominent firms in the chip/component segment include AMD, Hamamatsu, NanoQT, Nu Quantum, QBlox and Toptica. This report also analyzes the key technological trends that are spurring the success of neutral atom quantum computers. These include the use of photonic integrated circuits (PICs) to improve size, weight, and power consumption; novel materials platforms that can best support neutral atom machines; and the transition of neutral atom machines from large government and research facilities usage to HPC and the data center. What really matters for neutral atom quantum computers is that $/Qubit continues to be attractive. IQT Research notes that neutral atom technology is portrayed increasingly positively in the quantum trade press. For now, Amazon Braket and Azure Quantum are the only public ways to access a neutral atom quantum computer. Table of Contents
Report: IQT-NAQC2025-0525
Published: May 20, 2025
Table of Contents Neutral Atoms
Chapter One: Neutral Atom Technology and Products 1.1 Evolution of Technology 1.1.1 Atoms Used 1.1.2 Neutral Atoms Viewed Increasingly Positively 1.1.3 Accessibility 1.2 Neutral Atom Components 1.2.1 Atomic Control Hardware and Readout Components 1.2.2 Photonic and Photographic Components 1.2.3 Cryostats 1.3 Neutral Atom-related Software 1.3.1 Work in Research Labs Chapter Two: Markets and Origins 2.1 Target Applications and Possible Uses 2.1.1 Distributed Quantum Computing on Neutral Atom Computers 2.1.2 Neutral Atom Computers in the Data Center 2.1.3 Other Uses for Neutral Atom Computers 2.2 Of Control and Ecosystems 2.3 Supply Structure for Neutral Atom Computers 2.4 National Questions 2.4.1 Worldwide and National Markets for Neutral Atom Computers 2.4.2 The Question of Tariffs Chapter Three: Neutral Atom Technologies 3.1 Neutral Atom Computers 3.1.1 Atom Computing (United States) 3.1.2 Atom Quantum Labs (Slovenia) 3.1.3 Infleqtion (United States) 3.1.4 M Squared (United Kingdom) 3.1.5 OpenQuantum (United Kingdom) 3.1.6 Pasqal (France) 3.1.7 PlanQC (Germany) 3.1.8 QuEra Computing (United States) 3.2 Neutral Atom Components and Subsystems 3.2.1 AMD (United States) 3.2.2 Hamamatsu (Japan) 3.2.3 Lake Shore Cryotronics (United States) 3.2.4 MenloSystems (Germany) 3.2.5 NanoQT (Japan) 3.2.6 Nexus Photonics (United States) 3.2.7 Nu Quantum (United Kingdom) 3.2.8 OpenQuantum (Global) 3.2.9 Qblox (The Netherlands) 3.2.10 Quantum Machines (Israel) 3.2.11 Sandia National Laboratories (United States) 3.2.12 Toptica Photonics (Germany) 3.2.13 Vescent (United States) 3.3 Software 3.3.1 Agnostiq (Canada) 3.3.2 DarkStarStrix (username) (United States) 3.3.3 data cybernetics ssc GmbH (Germany) 3.3.4 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) (United States) 3.3.5 M-Labs (Hong Kong) 3.3.6 Microsoft (United States) 3.3.7 Q-CTRL (Australia) 3.3.8 QMWare (Switzerland) 3.3.9 QPerfect (France) 3.3.10 SimuQ (United States) 3.3.11 Wolfram (United States) 3.4 Platforms 3.4.1 Amazon Braket (United States) 3.4.2 qBraid (United States) 3.4.3 Strangeworks (United States) 3.5 National and International Centers 3.5.1 Department of Science and Technology (DOST) (Philippines) 3.5.2 European Center for Quantum Sciences (CESQ) (France) 3.5.3 Japan Science and Technology Agency (Japan) 3.5.4 National Quantum Computing Centre (NQCC) (United Kingdom) 3.5.5 Russian Quantum Center (Russia) Chapter Four: Ten-year Forecasts of Neutral Atom Computer 4.1 Forecasting Thoughts 4.2 Forecasts, their Uses and Uncertainties About the Analyst Exhibit Exhibit 4-1: Ten-year Forecasts of Neutral Atom Quantum Computers
Press Release
IQT RESEARCH ANNOUNCES NEW REPORT ON NEUTRAL ATOM QUANTUM COMPUTERS;
Nertral Atom Quantum Computers Shipped:2025
ご注文は、お電話またはWEBから承ります。お見積もりの作成もお気軽にご相談ください。本レポートと同分野の最新刊レポート
Inside Quantum Technology社の 市場レポート分野 での最新刊レポート
よくあるご質問Inside Quantum Technology社はどのような調査会社ですか?米国調査会社インサイドクァンタムテクノロジー(Inside Quantum Technology)は、量子コンピュータシステム、量子暗号デバイスとソフトウェア、量子センサなど量子技術に関連する情報を提... もっと見る 調査レポートの納品までの日数はどの程度ですか?在庫のあるものは速納となりますが、平均的には 3-4日と見て下さい。
注文の手続きはどのようになっていますか?1)お客様からの御問い合わせをいただきます。
お支払方法の方法はどのようになっていますか?納品と同時にデータリソース社よりお客様へ請求書(必要に応じて納品書も)を発送いたします。
データリソース社はどのような会社ですか?当社は、世界各国の主要調査会社・レポート出版社と提携し、世界各国の市場調査レポートや技術動向レポートなどを日本国内の企業・公官庁及び教育研究機関に提供しております。
|
|